Cytoplasmic transport of Stat3 by receptor-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 12093727
- PMCID: PMC126099
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf351
Cytoplasmic transport of Stat3 by receptor-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
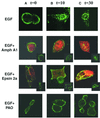
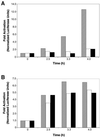
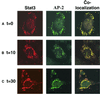
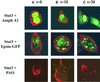
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins are cytoplasmic transcription factors that translocate to the nucleus and regulate gene expression upon activation of cytokine or growth factor receptors. While this translocation event is essential for gene regulation by STATs, their mechanism of transport through the cytoplasm to the nucleus has remained elusive. We now report that cytoplasmic transport of Stat3 is an active process that requires receptor-mediated endocytosis. Stat3 co-localizes with endocytic vesicles in transit from the cell membrane to the perinuclear region in response to growth factor stimulation. Consistent with a role for receptor endocytosis in growth factor signaling, disruption of endocytosis with specific inhibitors blocks Stat3 nuclear translocation and Stat3-dependent gene regulation. These results indicate that receptor-mediated endocytosis may be a general mechanism of transport through the cytoplasm for a subset of cytoplasmic signaling proteins destined for the nucleus.
Figures



References
-
- Bowman T., Garcia,R., Turkson,J. and Jove,R. (2000) STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene, 19, 2474–2488. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg J.F., Wrzeszczynska,M.H., Devgan,G., Zhao,Y., Pestell,R.G., Albanese,C. and Darnell,J.E.,Jr (1999) Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell, 98, 295–303. - PubMed
-
- Cahill M.A., Janknecht,R. and Nordheim,A. (1996) Signalling pathways: Jack of all cascades. Curr. Biol., 6, 16–19. - PubMed
-
- Ceresa B.P. and Schmid,S.L. (2000) Regulation of signal transduction by endocytosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 12, 204–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

