A growth factor-dependent nuclear kinase phosphorylates p27(Kip1) and regulates cell cycle progression
- PMID: 12093740
- PMCID: PMC126092
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf343
A growth factor-dependent nuclear kinase phosphorylates p27(Kip1) and regulates cell cycle progression
Abstract
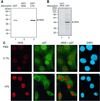
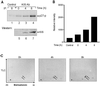
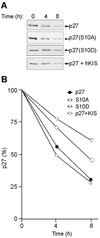
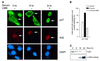
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p27(Kip1), which regulates cell cycle progression, is controlled by its subcellular localization and subsequent degradation. p27(Kip1) is phosphorylated on serine 10 (S10) and threonine 187 (T187). Although the role of T187 and its phosphorylation by Cdks is well-known, the kinase that phosphorylates S10 and its effect on cell proliferation has not been defined. Here, we identify the kinase responsible for S10 phosphorylation as human kinase interacting stathmin (hKIS) and show that it regulates cell cycle progression. hKIS is a nuclear protein that binds the C-terminal domain of p27(Kip1) and phosphorylates it on S10 in vitro and in vivo, promoting its nuclear export to the cytoplasm. hKIS is activated by mitogens during G(0)/G(1), and expression of hKIS overcomes growth arrest induced by p27(Kip1). Depletion of KIS using small interfering RNA (siRNA) inhibits S10 phosphorylation and enhances growth arrest. p27(-/-) cells treated with KIS siRNA grow and progress to S/G(2 )similar to control treated cells, implicating p27(Kip1) as the critical target for KIS. Through phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) on S10, hKIS regulates cell cycle progression in response to mitogens.
Figures







References
-
- Carrano A.C., Eytan,E., Hershko,A. and Pagano,M. (1999) SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 193–199. - PubMed
-
- Chneiweiss H., Cordier,J. and Sobel,A. (1992) Stathmin phosphorylation is regulated in striatal neurons by vasoactive intestinal peptide and monoamines via multiple intracellular pathways. J. Neurochem., 58, 282–289. - PubMed
-
- Cooper H.L., Fuldner,R., McDuffie,E. and Braverman,R. (1991) T cell receptor activation induces rapid phosphorylation of prosolin, which mediates down-regulation of DNA synthesis in proliferating peripheral lymphocytes. J. Immunol., 146, 3689–3696. - PubMed
-
- Doye V., Boutterin,M.C. and Sobel,A. (1990) Phosphorylation of stathmin and other proteins related to nerve growth factor-induced regulation of PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem., 265, 11650–11655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

