Increased ABCA1 activity protects against atherosclerosis
- PMID: 12093886
- PMCID: PMC151034
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15748
Increased ABCA1 activity protects against atherosclerosis
Abstract
The ABC transporter ABCA1 plays a key role in the first steps of the reverse cholesterol transport pathway by mediating lipid efflux from macrophages. Previously, it was demonstrated that human ABCA1 overexpression in vivo in transgenic mice results in a mild elevation of plasma HDL levels and increased efflux of cholesterol from macrophages. In this study, we determined the effect of overexpression of ABCA1 on atherosclerosis development. Human ABCA1 transgenic mice (BAC(+)) were crossed with ApoE(-/-) mice, a strain that spontaneously develop atherosclerotic lesions. BAC(+)ApoE(-/-) mice developed dramatically smaller, less-complex lesions as compared with their ApoE(-/-) counterparts. In addition, there was increased efflux of cholesterol from macrophages isolated from the BAC(+)ApoE(-/-) mice. Although the increase in plasma HDL cholesterol levels was small, HDL particles from BAC(+)ApoE(-/-) mice were significantly better acceptors of cholesterol. Lipid analysis of HDL particles from BAC(+)ApoE(-/-) mice revealed an increase in phospholipid levels, which was correlated significantly with their ability to enhance cholesterol efflux.
Figures
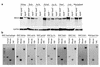
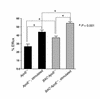


References
-
- Gordon DJ, et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease — four prospective American studies. Circulation. 1989;79:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Fielding CJ, Fielding PE. Intracellular cholesterol transport. J Lipid Res. 1997;38:1503–1521. - PubMed
-
- Cockerill GW, Rye KA, Gamble JR, Vadas MA, Barter PJ. High-density lipoproteins inhibit cytokine-induced expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:1987–1994. - PubMed
-
- Stary HC, et al. A definition of initial, fatty streak and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14:840–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

