Direct visualization of distinct T cell epitopes derived from a melanoma tumor-associated antigen by using human recombinant antibodies with MHC- restricted T cell receptor-like specificity
- PMID: 12093904
- PMCID: PMC123156
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.132285699
Direct visualization of distinct T cell epitopes derived from a melanoma tumor-associated antigen by using human recombinant antibodies with MHC- restricted T cell receptor-like specificity
Abstract
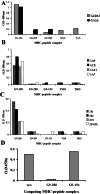
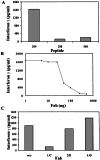
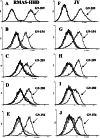
Specificity in the cellular immune system is controlled and regulated by the T cell antigen receptor (TCR), which specifically recognizes peptide/major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. In recent years many cancer-associated MHC-restricted peptides have been isolated and because of their highly restricted fine specificity, they are desirable targets for novel approaches in immunotherapy. Antibodies that would recognize tumor-associated MHC-peptide complexes with the same specificity as the TCR would be valuable reagents for studying antigen presentation by tumor cells, for visualizing MHC-peptide complexes on cells, and eventually for monitoring the expression of specific complexes during immunotherapy. To generate molecules with such a unique fine specificity, we selected a large nonimmune repertoire of phage Fab antibodies on recombinant HLA-A2 complexed with three common antigenic T cell, HLA-A2-restricted epitopes derived from the melanoma differentiation antigen gp100. We were able to isolate a surprisingly large panel of human recombinant Fab antibodies that exhibit a characteristic TCR-like binding specificity to each of the three gp100-derived epitopes, yet unlike TCRs, they did so with an affinity in the nanomolar range. These TCR-like antibodies recognize the native MHC-peptide complex expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. Moreover, they can detect the specific MHC-peptide complexes on the surface of melanoma tumor cells. These results demonstrate the ability to isolate high-affinity human recombinant antibodies with the antigen-specific, MHC-restricted specificity of T cells, and this ability was demonstrated for three different epitopes of the same melanoma-derived antigen.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenberg S A. Nature (London) 2001;411:380–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

