Knockout of the alpha 1A/C-adrenergic receptor subtype: the alpha 1A/C is expressed in resistance arteries and is required to maintain arterial blood pressure
- PMID: 12093905
- PMCID: PMC123165
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.132552699
Knockout of the alpha 1A/C-adrenergic receptor subtype: the alpha 1A/C is expressed in resistance arteries and is required to maintain arterial blood pressure
Abstract
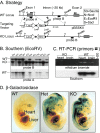
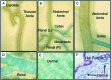
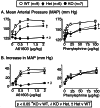
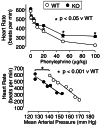
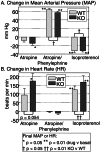
alpha 1-adrenergic receptors (ARs) play a major role in blood pressure regulation. The three alpha 1-AR subtypes (A/C, B, and D) stimulate contraction of isolated arteries, but it is uncertain how different subtypes contribute to blood pressure regulation in the intact animal. We studied the role of the alpha 1A/C subtype by using gene knockout. alpha 1A/C knockout (KO) mice were viable and overtly normal. The LacZ reporter gene replaced alpha 1A/C coding sequence in the KO, and beta-galactosidase staining was present in resistance arteries and arterioles, but not in the thoracic aorta or its main branches. By tail cuff manometer and arterial catheter in conscious mice, alpha 1A/C KO mice were hypotensive at rest, with an 8-12% reduction of blood pressure dependent on alpha 1A/C gene copy number. A61603, an alpha 1A/C-selective agonist, caused a pressor response that was lost in the KO and reduced but significant in heterozygous mice with a single copy of the alpha 1A/C. A subtype-nonselective agonist [phenylephrine (PE)] caused a pressor response in KO mice, but the final arterial pressure was only 85% of wild type. The baroreflex was reset in the KO, and heart rate variability was decreased. After baroreflex blockade with atropine, PE increased blood pressure but did not change heart rate. Cardiac and vascular responses to the beta-AR agonist isoproterenol were unchanged, and the arterial lumen area was not altered. We conclude that the alpha 1A/C-AR subtype is a vasopressor expressed in resistance arteries and is required for normal arterial blood pressure regulation. alpha 1A/C-selective antagonists might be desirable antihypertensive agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
α(1D)-Adrenoceptor regulates the vasopressor action of α(1A)-adrenoceptor in mesenteric vascular bed of α(1D)-adrenoceptor knockout mice.Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2011 Jul-Oct;31(3-4):64-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2011.00468.x. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21951586
-
The Alpha-1A Adrenergic Receptor in the Rabbit Heart.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 3;11(6):e0155238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155238. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27258143 Free PMC article.
-
Two alpha1-adrenergic receptor subtypes regulating the vasopressor response have differential roles in blood pressure regulation.Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Mar;67(3):912-22. doi: 10.1124/mol.104.007500. Epub 2004 Dec 14. Mol Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15598970
-
Insights into alpha1 adrenoceptor function in health and disease from transgenic animal studies.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Apr;14(3):107-13. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(03)00026-2. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12670735 Review.
-
Transgenic studies of alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor subtype function.Life Sci. 2002 Sep 27;71(19):2207-15. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)02012-x. Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12215368 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced alpha-adrenoceptor responsiveness and enhanced baroreflex sensitivity in Cry-deficient mice lacking a biological clock.J Physiol. 2005 Jul 1;566(Pt 1):213-24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.086728. Epub 2005 Apr 28. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15860530 Free PMC article.
-
Constraints of vigilance-dependent noradrenergic signaling to mouse cerebellar Bergmann glia.Glia. 2023 Jun;71(6):1451-1465. doi: 10.1002/glia.24350. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Glia. 2023. PMID: 36790089 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-1-adrenergic receptors in heart failure: the adaptive arm of the cardiac response to chronic catecholamine stimulation.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;63(4):291-301. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000032. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24145181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smooth muscle alpha1D-adrenoceptors mediate phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction and increases in endothelial cell Ca2+ in hamster cremaster arterioles.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;155(4):514-24. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.276. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18604236 Free PMC article.
-
The α₁B -adrenoceptor subtype mediates adrenergic vasoconstriction in mouse retinal arterioles with damaged endothelium.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;171(16):3858-67. doi: 10.1111/bph.12743. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24749494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guthrie R M, Siegel R L. Clin Ther. 1999;21:1732–1748. - PubMed
-
- ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. J Am Med Assoc. 2000;283:1967–1975. - PubMed
-
- Rokosh D G, Bailey B A, Stewart A F R, Karns L R, Long C S, Simpson P C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;200:1177–1184. - PubMed
-
- Michelotti G A, Price D T, Schwinn D A. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;88:281–309. - PubMed
-
- Piascik M T, Soltis E E, Piascik M M, Macmillan L B. Pharmacol Ther. 1996;72:215–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

