Melanin-concentrating hormone depresses L-, N-, and P/Q-type voltage-dependent calcium channels in rat lateral hypothalamic neurons
- PMID: 12096069
- PMCID: PMC2290404
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.019372
Melanin-concentrating hormone depresses L-, N-, and P/Q-type voltage-dependent calcium channels in rat lateral hypothalamic neurons
Abstract
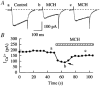
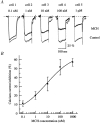
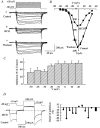
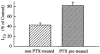
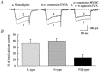
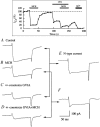
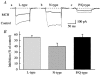
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), a cyclic 19-amino-acid peptide, is synthesized exclusively by neurons in the lateral hypothalamic (LH) area. It is involved in a number of brain functions and recently has raised interest because of its role in energy homeostasis. MCH axons and receptors are found throughout the brain. Previous reports set the foundation for understanding the cellular actions of MCH by using non-neuronal cells transfected with the MCH receptor gene; these cells exhibited an increase in cytoplasmic calcium in response to MCH, suggesting an excitatory action for the peptide. In the study presented here, we have used whole-cell recording in 117 neurons from LH cultures and brain slices to examine the actions of MCH. MCH decreased the amplitude of voltage-dependent calcium currents in almost all tested neurons. The inhibition desensitized rapidly (18 s to half maximum at 100 nM concentration) and was dose-dependent (IC(50) = 7.8 nM) when activated with a pulse from -80 mV to 0 mV. A priori activation of G-proteins with GTPgammaS completely eliminated the MCH-induced effect at low MCH concentrations and reduced the MCH-induced effect at high MCH concentrations. Inhibition of G-proteins with pertussis toxin (PTX) blocked the MCH-induced inhibitory effect at high MCH concentrations. Pre-pulse depolarization resulted in an attenuation of the MCH-induced inhibition of calcium currents in most neurons. These data suggest that MCH exerts an inhibitory effect on calcium currents via PTX-sensitive G-protein pathways, probably the G(i)/G(o) pathway, in LH neurons. L-, N- and P/Q-type calcium channels were identified in LH neurons, with L- and N-type channels accounting for most of the voltage-activated current (about 40 % each); MCH attenuated each of the three types (mean 50 % depression), with the greatest inhibition found for N-type currents. In contrast to previous data on non-neuronal cells showing an MHC-evoked increase in calcium, our data suggest that the reverse occurs in LH neurons. The attenuation of calcium currents is consistent with an inhibitory action for the peptide in neurons.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Melanin concentrating hormone depresses synaptic activity of glutamate and GABA neurons from rat lateral hypothalamus.J Physiol. 2001 May 15;533(Pt 1):237-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0237b.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11351031 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of serotonin on caudal raphe neurons: inhibition of N- and P/Q-type calcium channels and the afterhyperpolarization.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Mar;77(3):1362-74. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.3.1362. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9084603
-
Melanin concentrating hormone innervation of caudal brainstem areas involved in gastrointestinal functions and energy balance.Neuroscience. 2005;135(2):611-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.06.055. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 16111819
-
Electrophysiological effects of MCH on neurons in the hypothalamus.Peptides. 2009 Nov;30(11):2025-30. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.006. Epub 2009 May 20. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19463877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of food intake by melanin-concentrating hormone in goldfish.Peptides. 2009 Nov;30(11):2060-5. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.02.015. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19836661 Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral hypothalamic orexin and melanin-concentrating hormone neurons provide direct input to gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons in the human.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Sep 4;9:348. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00348. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26388735 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of synaptic efficacy in hypocretin/orexin-containing neurons by melanin concentrating hormone in the lateral hypothalamus.J Neurosci. 2008 Sep 10;28(37):9101-10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1766-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18784290 Free PMC article.
-
Melanin-concentrating hormone directly inhibits GnRH neurons and blocks kisspeptin activation, linking energy balance to reproduction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 6;106(40):17217-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908200106. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19805188 Free PMC article.
-
VGAT and VGLUT2 expression in MCH and orexin neurons in double transgenic reporter mice.IBRO Rep. 2018 May 12;4:44-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ibror.2018.05.001. eCollection 2018 Jun. IBRO Rep. 2018. PMID: 30155524 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide transmission in brain circuits.Neuron. 2012 Oct 4;76(1):98-115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.014. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23040809 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TA, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell. 1997;88:615–626. - PubMed
-
- Ahlijanian MK, Westenbroek RE, Catterall WA. Subunit structure and localization of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in mammalian brain, spinal cord, and retina. Neuron. 1990;4:819–832. - PubMed
-
- Bächner D, Kreienkamp H, Weise C, Buck F, Richter D. Identification of melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) as the natural ligand for the orphan somatostatin-like receptor 1 (SLC-1) FEBS Letters. 1999;457:522–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

