Differential presynaptic inhibition of actions of group II afferents in di- and polysynaptic pathways to feline motoneurones
- PMID: 12096070
- PMCID: PMC2315796
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.014068
Differential presynaptic inhibition of actions of group II afferents in di- and polysynaptic pathways to feline motoneurones
Abstract
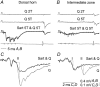
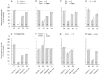
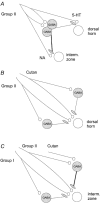
The aim of this study was to investigate differences in the effects of presynaptic inhibition of transmission from group II muscle afferents to neurones in the dorsal horn and in the intermediate zone and the consequences of these differences for reflex actions of group II afferents upon alpha-motoneurones. The degree of presynaptic inhibition was estimated from the degree of depression of monosynaptic components of population EPSPs (field potentials) evoked by group II muscle afferents in deeply anaesthetized cats. The decrease in the area of field potentials was considerably larger and longer lasting in the intermediate zone, where they were often obliterated, than in the dorsal horn, where they were reduced to about two-thirds. Presynaptic inhibition of field potentials evoked by other afferents at the same locations was much weaker. Intracellular records from alpha-motoneurones revealed that short latency EPSPs and IPSPs evoked from group II afferents are considerably reduced by conditioning stimuli that effectively depress intermediate zone field potentials of group II origin. The results of this study lead to the conclusion that strong presynaptic inhibition of transmission to intermediate zone interneurones allows a selective depression of disynaptic actions of group II muscle afferents on alpha- and gamma-motoneurones, mediated by these interneurones, and favours polysynaptic actions of these afferents.
Figures

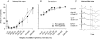


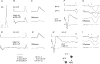
References
-
- Bras H, Jankowska E, Noga B, Skoog B. Comparison of effects of various types of NA and 5-HT agonists on transmission from group II muscle afferents in the cat. European Journal of Neuroscience. 1990;2:1029–1039. - PubMed
-
- Curtis DR, Lacey G. Prolonged GABA(B) receptor-mediated synaptic inhibition in the cat spinal cord: an in vivo study. Experimental Brain Research. 1998;121:319–333. - PubMed
-
- Eccles R, Lundberg A. Synaptic actions in motoneurones by afferents which may evoke the flexion reflex. Archives Italiennes de Biologie. 1959;97:199–221.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

