Lymphopenia in the BB rat model of type 1 diabetes is due to a mutation in a novel immune-associated nucleotide (Ian)-related gene
- PMID: 12097339
- PMCID: PMC186618
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.412702
Lymphopenia in the BB rat model of type 1 diabetes is due to a mutation in a novel immune-associated nucleotide (Ian)-related gene
Abstract
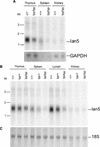
The BB (BioBreeding) rat is one of the best models of spontaneous autoimmune diabetes and is used to study non-MHC loci contributing to Type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes in the diabetes-prone BB (BBDP) rat is polygenic, dependent upon mutations at several loci. Iddm1, on chromosome 4, is responsible for a lymphopenia (lyp) phenotype and is essential to diabetes. In this study, we report the positional cloning of the Iddm1/lyp locus. We show that lymphopenia is due to a frameshift deletion in a novel member (Ian5) of the Immune-Associated Nucleotide (IAN)-related gene family, resulting in truncation of a significant portion of the protein. This mutation was absent in 37 other inbred rat strains that are nonlymphopenic and nondiabetic. The IAN gene family, lying within a tight cluster on rat chromosome 4, mouse chromosome 6, and human chromosome 7, is poorly characterized. Some members of the family have been shown to be expressed in mature T cells and switched on during thymic T-cell development, suggesting that Ian5 may be a key factor in T-cell development. The lymphopenia mutation may thus be useful not only to elucidate Type 1 diabetes, but also in the function of the Ian gene family as a whole.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alighment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bellgrau D, Naji A, Silvers WK, Markmann JF, Barker CF. Spontaneous diabetes in BB rats: Evidence for a T cell dependent immune response defect. Diabetologia. 1982;23:359–364. - PubMed
-
- Bieg S, Möller C, Olsson T, Lernmark Å. The lymphopenia (lyp) gene controls the intrathymic cytokine ratio in congenic BioBreeding rats. Diabetologia. 1997;40:786–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
