Transgenic calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activation: dose-dependent effects on synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory
- PMID: 12097524
- PMCID: PMC6758231
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05719.2002
Transgenic calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activation: dose-dependent effects on synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory
Abstract
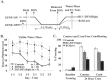
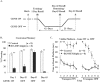
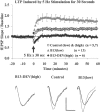
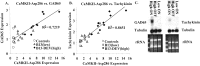
Genetic disruption of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) function alters hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory in mice. We used transgenic mice carrying a tetracycline-regulated, calcium-independent form of CaMKII (CaMKII-Asp286) to investigate the role of CaMKII activation on synaptic plasticity and behavior. Mice expressing low levels of a CaMKII-Asp286 transgene have facilitated low-frequency (5 Hz)-induced long-term potentiation (LTP), whereas mice with high levels of transgene expression have a deficit in this form of plasticity. Behavioral impairments on fear-conditioned memory and visible water maze correlate with the level of CaMKII-Asp286 expression. Mice with high levels of CaMKII-Asp286 have reversible, compensatory changes in the expression of genes associated with inhibitory neurotransmission. These results demonstrate that in the hippocampus, CaMKII activation facilitates the induction of low-frequency LTP, but at high levels of expression, compensatory mechanisms act to inhibit the induction of this form of LTP. The most severe behavioral impairments are associated with activation of this compensatory mechanism.
Figures


References
-
- Bach ME, Hawkins RD, Osman M, Kandel ER, Mayford M. Impairment of spatial but not contextual memory in CaMKII mutant mice with a selective loss of hippocampal LTP in the range of the theta frequency. Cell. 1995;81:905–915. - PubMed
-
- Devan BD, Goad EH, Petri HL. Dissociation of hippocampal and striatal contributions to spatial navigation in the water maze. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1996;66:305–323. - PubMed
-
- Devan BD, McDonald RJ, White NM. Effects of medial and lateral caudate-putamen lesions on place- and cue-guided behaviors in the water maze: relation to thigmotaxis. Behav Brain Res. 1999;100:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Enslen H, Soderling TR. Roles of calmodulin-dependent protein kinases and phosphatase in calcium-dependent transcription of immediate early genes. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20872–20877. - PubMed
-
- Enslen H, Sun P, Brickey D, Soderling SH, Klamo E, Soderling TR. Characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. IV. Role in transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:15520–15527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
