RNA editing in hepatitis delta virus genotype III requires a branched double-hairpin RNA structure
- PMID: 12097551
- PMCID: PMC136351
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7385-7397.2002
RNA editing in hepatitis delta virus genotype III requires a branched double-hairpin RNA structure
Abstract
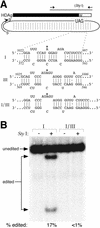
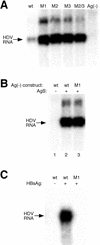
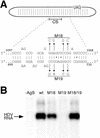
RNA editing at the amber/W site plays a central role in the replication scheme of hepatitis delta virus (HDV), allowing the virus to produce two functionally distinct forms of the sole viral protein, hepatitis delta antigen (HDAg), from the same open reading frame. Editing is carried out by a cellular activity known as ADAR (adenosine deaminase), which acts on RNA substrates that are at least partially double stranded. In HDV genotype I, editing requires a highly conserved base-paired structure that occurs within the context of the unbranched rod structure characteristic of HDV RNA. This base-paired structure is disrupted in the unbranched rod of HDV genotype III, which is the most distantly related of the three known HDV genotypes and is associated with the most severe disease. Here I show that RNA editing in HDV genotype III requires a branched double-hairpin structure that deviates substantially from the unbranched rod structure, involving the rearrangement of nearly 80 bp. The structure includes a UNCG RNA tetraloop, a highly stable structural motif frequently involved in the folding of large RNAs such as rRNA. The double-hairpin structure is required for editing, and hence for virion formation, but not for HDV RNA replication, which requires the unbranched rod structure. HDV genotype III thus relies on a dynamic conformational switch between the two different RNA structures: the unbranched rod characteristic of HDV RNA and a branched double-hairpin structure that is required for RNA editing. The different mechanisms of editing in genotypes I and III underscore their functional differences and may be related to pathogenic differences as well.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential inhibition of RNA editing in hepatitis delta virus genotype III by the short and long forms of hepatitis delta antigen.J Virol. 2003 Jul;77(14):7786-95. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.14.7786-7795.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12829818 Free PMC article.
-
The role of a metastable RNA secondary structure in hepatitis delta virus genotype III RNA editing.RNA. 2006 Aug;12(8):1521-33. doi: 10.1261/rna.89306. Epub 2006 Jun 21. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16790843 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis delta virus RNA editing is highly specific for the amber/W site and is suppressed by hepatitis delta antigen.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Apr;18(4):1919-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.1919. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9528763 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing in hepatitis delta virus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;307:67-89. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29802-9_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16903221 Review.
-
Control of ADAR1 editing of hepatitis delta virus RNAs.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;353:123-43. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_146. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21732238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eighth major clade for hepatitis delta virus.Emerg Infect Dis. 2006 Sep;12(9):1447-50. doi: 10.3201/eid1209.060112. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 17073101 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Factors Involved in the Hepatitis D Virus Life Cycle.Viruses. 2023 Aug 3;15(8):1687. doi: 10.3390/v15081687. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA conformational changes in the life cycles of RNA viruses, viroids, and virus-associated RNAs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Sep-Oct;1789(9-10):571-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19501200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Design Using incaRNAfbinv Demonstrated with the Identification of Functional RNA Motifs in Hepatitis Delta Virus.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2847:109-120. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4079-1_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39312139
-
Host-mediated RNA editing in viruses.Biol Direct. 2023 Mar 28;18(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00366-w. Biol Direct. 2023. PMID: 36978112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelkafi, M., N. Leulliot, V. Baumruk, L. Bednarova, P. Y. Turpin, A. Namane, C. Gouyette, T. Huynh-Dinh, and M. Ghomi. 1998. Structural features of the UCCG and UGCG tetraloops in very short hairpins as evidenced by optical spectroscopy. Biochemistry 37:7878-7884. - PubMed
-
- Been, M. D., and G. S. Wickham. 1997. Self-cleaving ribozymes of hepatitis delta virus RNA. Eur. J. Biochem. 247:741-753. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann, K. F., and J. L. Gerin. 1986. Antigens of hepatitis delta virus in the liver and serum of humans and animals. J. Infect. Dis. 154:702-706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

