Kinetics and frequency of adeno-associated virus site-specific integration into human chromosome 19 monitored by quantitative real-time PCR
- PMID: 12097568
- PMCID: PMC136374
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7554-7559.2002
Kinetics and frequency of adeno-associated virus site-specific integration into human chromosome 19 monitored by quantitative real-time PCR
Abstract
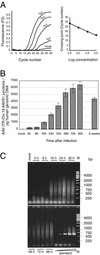
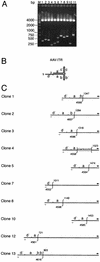
Adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV-2) integrates specifically into a site on human chromosome 19 (chr-19) called AAVS1. To study the kinetics and frequency of chr-19-specific integration after AAV infection, we developed a rapid, sensitive, and quantitative real-time PCR assay for AAV inverted terminal repeat-chr-19-specific junctions. Despite the known variability of junction sites, conditions were established that ensured reliable quantification of integration rates within hours after AAV infection. The overall integration frequency was calculated to peak at between 10 and 20% of AAV-infected, unselected HeLa cells. At least 1 in 1,000 infectious AAV-2 particles was found to integrate site specifically up to day 4 postinfection in the absence of selection. Chromosomal breakpoints within AAVS1 agreed with those found in latently infected clonal cell lines and transgenic animals. Use of this quantitative real-time PCR will greatly facilitate the study of the early steps of wild-type and recombinant AAV vector integration.
Figures


References
-
- Berns, K. I. 1996. Parvoviridae: the viruses and their replication, p. 2173-2197. In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, et al. (ed.), Fields virology. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Grimm, D., A. Kern, K. Rittner, and J. A. Kleinschmidt. 1998. Novel tools for production and purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 9:2745-2760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

