Transgenic expression of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus genes in H-2(b) mice inhibits resistance to virus-induced demyelination
- PMID: 12097592
- PMCID: PMC136370
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7799-7811.2002
Transgenic expression of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus genes in H-2(b) mice inhibits resistance to virus-induced demyelination
Abstract
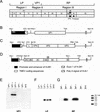
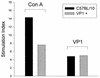
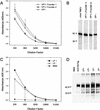
We investigated the role of the immune system in protecting against virus-induced demyelination by generating lines of transgenic B10 (H-2(b)) congenic mice expressing three independent contiguous coding regions of the Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) under the control of a class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) promoter. TMEV infection of normally resistant B10 mice results in virus clearance and development of inflammatory demyelination in the spinal cord. Transgenic expression of the viral capsid genes resulted in inactivation of virus-specific CD8(+) T lymphocytes (class I MHC immune function) directed against the relevant peptides, but it did not affect production of virus capsid-specific antibodies or lymphocyte proliferation to the virus antigen (class II MHC immune functions). Following intracerebral infection with TMEV, all three lines of mice survived the acute encephalitis but transgenic mice expressing VP1 (or the cluster of virus capsid proteins [VP4, VP2, and VP3] mapping to the left of VP1 in the TMEV genome) developed virus persistence and subsequent demyelination in spinal cord white matter. Transgenic mice expressing noncapsid proteins mapping to the right of VP1 (2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, 3C, and 3D) cleared the virus and did not develop demyelination. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that virus capsid gene products of TMEV stimulate class I-restricted CD8(+) T-cell immune responses, which are important for virus clearance and for protection against myelin destruction. Presented within the context of self-antigens, inactivation of these cells by ubiquitous expression of relevant virus capsid peptides partially inhibited resistance to virus-induced demyelination.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Class II-restricted T cell responses in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease. VI. Potentiation of demyelination with and characterization of an immunopathologic CD4+ T cell line specific for an immunodominant VP2 epitope.J Immunol. 1994 Jan 15;152(2):919-29. J Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7506740
-
Class II-restricted T cell responses in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease. IV. Identification of an immunodominant T cell determinant on the N-terminal end of the VP2 capsid protein in susceptible SJL/J mice.J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2401-8. J Immunol. 1991. PMID: 1706400
-
Gamma interferon is critical for neuronal viral clearance and protection in a susceptible mouse strain following early intracranial Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus infection.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(22):12252-65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.12252-12265.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14581562 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease in mice.Intervirology. 1997;40(2-3):143-52. doi: 10.1159/000150541. Intervirology. 1997. PMID: 9450231 Review.
-
Neuropathogenesis of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus infection, an animal model for multiple sclerosis.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;5(3):355-69. doi: 10.1007/s11481-009-9179-x. Epub 2009 Nov 6. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19894121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The immunodominant CD8+ T cell epitope region of Theiler's virus in resistant C57BL/6 mice is critical for anti-viral immune responses, viral persistence, and binding to the host cells.Virology. 2007 Mar 30;360(1):159-71. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.09.045. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17095033 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic expression of non-structural genes of Theiler's virus suppresses initial viral replication and pathogenesis of demyelination.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Jun 1;13(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0597-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27250711 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic deletion of a single immunodominant T-cell response confers susceptibility to virus-induced demyelination.Brain Pathol. 2007 Apr;17(2):184-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00062.x. Brain Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17388949 Free PMC article.
-
Anticapsid immunity level, not viral persistence level, correlates with the progression of Theiler's virus-induced demyelinating disease in viral P1-transgenic mice.J Virol. 2008 Jun;82(11):5606-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02442-07. Epub 2008 Mar 19. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18353953 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic expression of viral capsid proteins predisposes to axonal injury in a murine model of multiple sclerosis.Brain Pathol. 2011 Sep;21(5):501-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00474.x. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Brain Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21314744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borson, N. D., C. Paul, X. Lin, W. K. Nevala, M. A. Strausbauch, M. Rodriguez, and P. J. Wettstein. 1997. Brain-infiltrating cytolytic T lymphocytes specific for Theiler's virus recognize H2Db molecules complexed with a viral VP2 peptide lacking a consensus anchor residue. J. Virol. 71:5244-5250. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gerety, S. J., R. J. Clatch, H. L. Lipton, R. G. Goswami, M. K. Rundell, and S. D. Miller. 1991. Class II-restricted T cell responses in Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease. IV. Identification of an immunodominant T cell determinant on the N-terminal end of the VP2 capsid protein in susceptible SJL/J mice. J. Immunol. 146:2401-2408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

