Intercellular calcium signaling mediated by point-source burst release of ATP
- PMID: 12097649
- PMCID: PMC125036
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152588599
Intercellular calcium signaling mediated by point-source burst release of ATP
Abstract
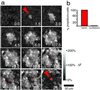
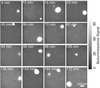
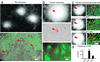
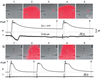
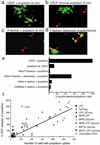
Calcium signaling, manifested as intercellular waves of rising cytosolic calcium, is, in many cell types, the result of calcium-induced secretion of ATP and activation of purinergic receptors. The mechanism by which ATP is released has hitherto not been established. Here, we show by real-time bioluminescence imaging that ATP efflux is not uniform across a field of cells but is restricted to brief, abrupt point-source bursts. The ATP bursts emanate from single cells and manifest the transient opening of nonselective membrane channels, which admits fluorescent indicators of < or = 1.5 kDa. These observations challenge the existence of regenerative ATP release, because ATP efflux is finite and restricted to a point source. Transient efflux of cytosolic nucleotides from a subset of cells may represent a conserved pathway for coordinating local activity of electrically nonexcitable cells, because identical patterns of ATP release were identified in human astrocytes, endothelial cells, and bronchial epithelial cells.
Figures
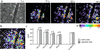
References
-
- Cornell-Bell A H, Finkbeiner S M, Cooper M S, Smith S J. Science. 1990;247:470–473. - PubMed
-
- Nedergaard M. Science. 1994;263:1768–1771. - PubMed
-
- Patel S, Robb-Gaspers L D, Stellato K A, Shon M, Thomas A P. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:467–471. - PubMed
-
- Kaneko T, Tanaka H, Oyamada M, Kawata S, Takamatsu T. Circ Res. 2000;86:1093–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

