The effect of rizatriptan, ergotamine, and their combination on human peripheral arteries: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in normal subjects
- PMID: 12100223
- PMCID: PMC1874381
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01403.x
The effect of rizatriptan, ergotamine, and their combination on human peripheral arteries: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in normal subjects
Abstract
Aims: To compare the peripheral vasoconstrictor effects of ergotamine, rizatriptan, and their combination, in normal subjects.
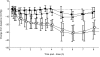
Methods: This was a double-blind, four-way, crossover study. Sixteen young male volunteers, selected as responders to the vasoconstrictor effect of 0.5 mg ergotamine i.v., were administered 10 mg oral rizatriptan, 0.25 mg i.v. ergotamine, 10 mg oral rizatriptan+0.25 mg i.v. ergotamine, and placebo. The vasoconstrictor effect on peripheral arteries was measured with strain gauge plethysmography up to 8 h after dosing. The 8 h assessment period was divided into two 4 h intervals to assess the immediate (0-4 h) vs sustained effect (4-8 h) of treatment.
Results: For the 0-4 h interval, the decreases in peripheral systolic blood pressure gradients were: placebo (-1 mmHg [95% CI: -3, 1])<rizatriptan (-5 mmHg [95% CI: -7, -3])<ergotamine (-15 mmHg [95% CI: -16, -13])=rizatriptan+ergotamine (-15 mmHg [95% CI: -17, -13]). For the 4-8 h interval, the decreases were: placebo (-5 mmHg [95% CI: -8, -3])=rizatriptan (-8 mmHg [95% CI: -11, -5])<ergotamine (-26 mmHg [95% CI: -29, -24])=rizatriptan+ergotamine (-28 mmHg [95% CI: -31, -26]).
Conclusions: In normal subjects, rizatriptan 10 mg orally had only a small transient vasoconstrictor effect on peripheral arteries compared with the sustained and more pronounced effect of 0.25 mg i.v. ergotamine. Furthermore, rizatriptan exerted no additional effect on ergotamine-induced constriction of peripheral arteries when the two drugs were given in combination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crossover comparison of efficacy and preference for rizatriptan 10 mg versus ergotamine/caffeine in migraine.Eur Neurol. 2003;49(1):20-9. doi: 10.1159/000067018. Eur Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12464714 Clinical Trial.
-
Crossover, double-blind clinical trial comparing almotriptan and ergotamine plus caffeine for acute migraine therapy.Eur J Neurol. 2007 Mar;14(3):269-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01594.x. Eur J Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17355546 Clinical Trial.
-
Vascular effects of 5-HT1B/1D-receptor agonists in patients with migraine headaches.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Oct;68(4):418-26. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2000.110502. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 11061582 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of rizatriptan and sumatriptan versus Cafergot in the acute treatment of migraine.CNS Drugs. 2005;19(7):635-42. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200519070-00005. CNS Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15984898 Review.
-
Rizatriptan: a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in the acute treatment of migraine.Pharmacoeconomics. 2005;23(12):1283-98. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200523120-00011. Pharmacoeconomics. 2005. PMID: 16336021 Review.
Cited by
-
Serotonin receptor agonists in the acute treatment of migraine: a review on their therapeutic potential.J Pain Res. 2018 Mar 8;11:515-526. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S132833. eCollection 2018. J Pain Res. 2018. PMID: 29563831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 5-HT1F receptor agonist lasmiditan as a potential treatment of migraine attacks: a review of two placebo-controlled phase II trials.J Headache Pain. 2012 Jun;13(4):271-5. doi: 10.1007/s10194-012-0428-7. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Headache Pain. 2012. PMID: 22430431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rizatriptan in the treatment of migraine.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006 Sep;2(3):247-59. doi: 10.2147/nedt.2006.2.3.247. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006. PMID: 19412472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saxena PR, Tfelt-Hansen P. Triptans, 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists, in the acute treatment of migraine. In: Olesen J, Tfelt-Hansen P, Welch KMA, editors. The Headaches. 2. New York: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2000. pp. 411–438.
-
- Tfelt-Hansen P, De Vries P, Saxena PR. Triptans in migraine. A comparative review of their pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Drugs. 2000;60:1259–1287. - PubMed
-
- Hamel E. Serotonin receptors. Relevance to migraine pathogenesis and treatment. In: Olesen J, Tfelt-Hansen P, Welch KMA, editors. The Headaches. 2. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2000. pp. 133–139.
-
- Humphrey PPA, Apperley E, Feniuk W, Perren MJ. A rational approach to identifying a fundamentally new drug for the treatment of migraine. In: Saxena PR, Wallis DI, Wouters W, Bevan P, editors. Cardiovascular Pharmacology of 5-Hydroxytryptamine: Prospective Therapeutic Applications. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1990. pp. 416–431.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources