Type I interferon gene therapy protects against cytomegalovirus-induced myocarditis
- PMID: 12100732
- PMCID: PMC1782722
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01423.x
Type I interferon gene therapy protects against cytomegalovirus-induced myocarditis
Abstract
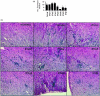
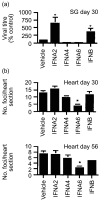
Type I interferons (IFNs) are produced early in response to viral infection and modulate adaptive immunity. Previously we demonstrated localized protection against murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection in IFN DNA-inoculated mice. Here we examine the effect of seven IFN subtypes (IFNA1, A2, A4, A5, A6, A9 and B), administered by DNA inoculation, on systemic MCMV infection and myocarditis. IFN transgene expression altered the pathogenesis of MCMV infection with regard to virus titre and myocarditis. IFNA6 treatment reduced MCMV replication whilst IFNA5 and A2 enhanced virus replication. IFNA6, A9, and B treatment inhibited acute myocarditis. A T helper type 1-like, antibody and cytokine, response correlated with decreased virus titre and myocarditis. In addition, IFNA6 was able to reduce chronic cardiac inflammation. This research into the effectiveness of seven type I IFNs, using DNA gene therapy, highlights the need for correct subtype usage in the treatment of disease. We demonstrate effective subtypes for treatment in both the acute and chronic phases of MCMV infection and the resultant development of myocarditis.
Figures

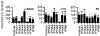
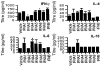
References
-
- Foster GR, Finter NB. Are all type I human IFNs equivalent? Rev J Viral Hepatitis. 1998;5:143–52. - PubMed
-
- Weissman C, Werber H. The interferon genes. Prog Nucl Acid Res. 1986;33:251–300. - PubMed
-
- Samuel CE. Antiviral actions of IFN. IFN-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991;183:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

