Requirement of macrophages and eosinophils and their cytokines/chemokines for mammary gland development
- PMID: 12100741
- PMCID: PMC138736
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr441
Requirement of macrophages and eosinophils and their cytokines/chemokines for mammary gland development
Abstract
Epithelial/mesenchymal cell interactions are necessary for proper ductal morphogenesis throughout all stages of mammary gland development. Besides the well-established stromal components, such as adipocytes and fibroblasts, the mammary stroma is also infiltrated with migrating blood cells, mostly macrophages and eosinophils. The focus of this review is on the role of macrophages and their growth factor colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) in promoting branching morphogenesis during postnatal mammary gland development through to lactation. The more restricted role of eosinophils and their chemoattractant eotaxin during pubertal ductal morphogenesis is also discussed. A possible interaction between macrophages and eosinophils in ductal morphogenesis is considered, along with the roles of other chemokines. This role of macrophages in normal development also appears to be subverted by tumors of the mammary gland to promote the escape of the tumor cells from the local environment and enhance their rate of metastasis. These data emphasize the dual role of macrophages in the promotion of epithelial growth in normal and cancer states.
Figures
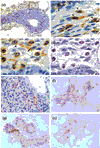
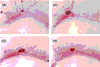
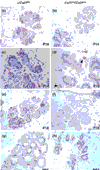

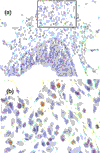
References
-
- Robinson GW, Karpf AB, Kratochwil K. Regulation of mammary gland development by tissue interaction. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1999;4:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Sakakura T, Sakagami Y, Nishizuka Y. Dual origin of mesenchymal tissues participating in mouse mammary gland embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1982;91:202–207. - PubMed
-
- Enami J, Enami S, Koga M. Growth of normal and neoplastic mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture: stimulation by conditioned medium from mouse mammary fibroblasts. Gann. 1983;74:845–853. - PubMed
-
- Levine JF, Stockdale FE. 3T3-L1 adipocytes promote the growth of mammary epithelium. Exp Cell Res. 1984;151:112–122. - PubMed
-
- Carrington CA, Hosick HL. Effects of dietary fat on the growth of normal, preneoplastic and neoplastic mammary epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1985;75:269–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

