CARD games in apoptosis and immunity
- PMID: 12101092
- PMCID: PMC1084193
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf139
CARD games in apoptosis and immunity
Abstract
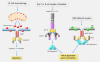
A bewildering array of proteins containing the caspase recruitment domain (CARD) have now been identified. Previously, CARD-CARD interactions have been shown to be involved in the assembly of protein complexes that promote caspase processing and activation in the context of apoptosis. However, as the family of CARD-containing proteins has grown, it has become apparent that the majority of these proteins do not recruit caspases or promote caspase activation. Instead, many participate in NF-kappaB signalling pathways associated with innate or adaptive immune responses. Here, we suggest a simplified classification of the CARD proteins based upon their domain structures and discuss the divergent roles of these proteins in the context of host defence.
Figures


References
-
- Aderem A. and Ulevitch, R.J. (2000) Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature, 406, 782–787. - PubMed
-
- Adrain C. and Martin, S.J. (2001) The mitochondrial apoptosome: a killer unleashed by the cytochrome seas. Trends Biochem. Sci., 26, 390–397. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L., Dixit, V.M. and Koonin, E.V. (1999) The domains of death: evolution of the apoptosis machinery. Trends Biochem. Sci., 24, 47–53. - PubMed
-
- Bertin J. and DiStefano, P.S. (2000) The PYRIN domain: a novel motif found in apoptosis and inflammation proteins. Cell Death Differ., 7, 1273–1274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

