MicroRNAs in plants
- PMID: 12101121
- PMCID: PMC186362
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1004402
MicroRNAs in plants
Erratum in
- Genes Dev 2002 Sep 1;16(17):2313
Abstract
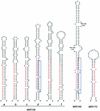
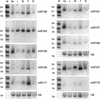
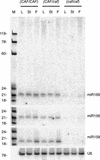
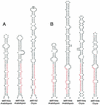
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are an extensive class of ~22-nucleotide noncoding RNAs thought to regulate gene expression in metazoans. We find that miRNAs are also present in plants, indicating that this class of noncoding RNA arose early in eukaryotic evolution. In this paper 16 Arabidopsis miRNAs are described, many of which have differential expression patterns in development. Eight are absolutely conserved in the rice genome. The plant miRNA loci potentially encode stem-loop precursors similar to those processed by Dicer (a ribonuclease III) in animals. Mutation of an Arabidopsis Dicer homolog, CARPEL FACTORY, prevents the accumulation of miRNAs, showing that similar mechanisms direct miRNA processing in plants and animals. The previously described roles of CARPEL FACTORY in the development of Arabidopsis embryos, leaves, and floral meristems suggest that the miRNAs could play regulatory roles in the development of plants as well as animals.
Figures
References
-
- The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- Aravin AA, Naumova NM, Tulin AA, Rozovsky YM, Gvozdev VA. Double-stranded RNA-mediated silencing of genomic tandem repeats and transposable elements in Drosophila melanogastergermline. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1017–1027. - PubMed
-
- Bender J. A vicious cycle: RNA silencing and DNA methylation in plants. Cell. 2001;106:129–132. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:295–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
