Oxygen-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor requires nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein
- PMID: 12101228
- PMCID: PMC133938
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5319-5336.2002
Oxygen-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor requires nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein
Abstract
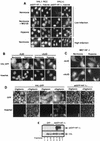
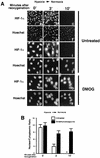
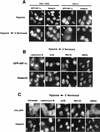
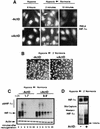
It is becoming increasingly evident that the degradation of nuclear proteins requires nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of both the substrate proteins, as well as the E3 ubiquitin-ligases. Here, we show that nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein (VHL) is required for oxygen-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of the alpha subunits of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-alpha). VHL engages in a constitutive transcription-sensitive nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttle unaffected by oxygen tension or levels of nuclear substrate HIF-alpha. Ubiquitinated forms of HIF-alpha, as well as VHL/ubiquitinated HIF-alpha complexes, are found solely in the nuclear compartment of normoxic or reoxygenated VHL-competent cells. HIF-alpha localizes exclusively in the nucleus of hypoxic cells but is exported to the cytoplasm upon reoxygenation. Oxygen-dependent nuclear ubiquitination and nuclear export of HIF-alpha can be prevented by treatment with an HIF-specific prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor. Treatment with inhibitors of RNA polymerase II activity, which interfere with the ability of VHL to engage in nuclear export, also prevents cytoplasmic accumulation of HIF-alpha in reoxygenated cells. This caused a marked increase in the HIF-alpha half-life without affecting its nuclear ubiquitination. We present a model by which VHL-mediated ubiquitination of HIF-alpha and its subsequent degradation are dependent upon dynamic nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of both the E3 ubiquitin-ligase and the nuclear substrate protein.
Figures




References
-
- Berra, E., D. E. Richard, E. Gothie, and J. Pouyssegur. 2001. HIF-1-dependent transcriptional activity is required for oxygen-mediated HIF-1α degradation. FEBS Lett. 491:85-90. - PubMed
-
- Blankenship, C., J. G. Naglich, J. M. Whaley, B. Seizinger, and N. Kley. 1999. Alternate choice of initiation codon produces a biologically active product of the von Hippel-Lindau gene with tumor suppressor activity. Oncogene 18:1529-1535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
