Neuronal differentiation and protection from nitric oxide-induced apoptosis require c-Jun-dependent expression of NCAM140
- PMID: 12101231
- PMCID: PMC133958
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5357-5366.2002
Neuronal differentiation and protection from nitric oxide-induced apoptosis require c-Jun-dependent expression of NCAM140
Abstract
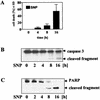
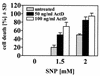
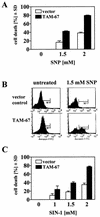
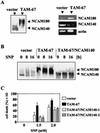
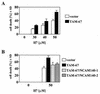
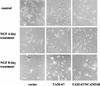
c-Jun, a crucial component of the dimeric transcription factor activating protein 1 (AP-1), can regulate apoptosis induced by oxidative stress and has been implicated in neuronal differentiation, but the mechanisms are largely unknown. We found that specific inhibition of transcription or stable transfection with cDNA encoding dominant-negative c-Jun sensitized SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (TAM-67 cells) to apoptosis induced by the nitric oxide (NO) donor sodium nitroprusside or SIN-1. TAM-67 cells also became refractory to nerve growth factor (NGF)-induced neuronal differentiation. Dominant-negative c-Jun abolished expression of a 140-kDa neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM140) and dramatically enhanced the expression of NCAM180 in TAM-67 cells. Inhibition of c-Jun in TAM-67 cells also resulted in a corresponding decrease in the amount of NCAM140 mRNA and an increase in the amount of NCAM180 mRNA. Reexpression of NCAM140 in TAM-67 cells restored NGF-induced neuronal differentiation and resistance to NO-induced apoptosis. Our results show that c-Jun/AP-1, through up-regulation of NCAM140, plays an important role in both NGF-induced neuronal differentiation and resistance to apoptosis induced by NO in neuroblastoma cells. As NCAM140 and NCAM180 are translated from differentially spliced mRNAs transcribed from the same gene, alternative splicing of NCAM pre-mRNA (and consequently the synthesis of the smaller NCAM140 species) appears to be regulated by c-Jun/AP-1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
JNK-dependent phosphorylation of c-Jun on serine 63 mediates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 6;279(6):4058-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310415200. Epub 2003 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14617628
-
Secretogranin II: a key AP-1-regulated protein that mediates neuronal differentiation and protection from nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells.Cell Death Differ. 2008 May;15(5):879-88. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.8. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Cell Death Differ. 2008. PMID: 18239671
-
Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) association with PKCbeta2 via betaI spectrin is implicated in NCAM-mediated neurite outgrowth.J Cell Biol. 2003 May 12;161(3):625-39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200303020. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12743109 Free PMC article.
-
Direct inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in sympathetic neurones prevents c-jun promoter activation and NGF withdrawal-induced death.J Neurochem. 2001 Mar;76(5):1439-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00150.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11238729
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase-dependent activation of c-Jun and c-Fos is required for neuronal differentiation but not for growth and stress response in PC12 cells.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Feb;210(2):538-48. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20907. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17111371
Cited by
-
Neural cell adhesion molecule isoform 140 declines with rise of WHO grade in human gliomas and serves as indicator for the invasion zone of multiform glioblastomas and brain metastases.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011 Mar;137(3):399-414. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0888-6. Epub 2010 May 4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 20440511 Free PMC article.
-
Unfavorable neuroblastoma prognostic factor NLRR2 inhibits cell differentiation by transcriptional induction through JNK pathway.Cancer Sci. 2016 Sep;107(9):1223-32. doi: 10.1111/cas.13003. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27357360 Free PMC article.
-
Protein/DNA arrays identify nitric oxide-regulated cis-element and trans-factor activities some of which govern neuroblastoma cell viability.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(16):5439-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm594. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17702766 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of synaptic nlg-1/neuroligin abundance by the skn-1/Nrf stress response pathway protects against oxidative stress.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1004100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004100. Epub 2014 Jan 16. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24453991 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for severity of spinal cord injury in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 29;6(4):e19247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019247. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21559420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ankarcrona, M., J. M. Dypbukt, E. Bonfoco, B. Zhivotovsky, S. Orrenius, S. A. Lipton, and P. Nicotera. 1995. Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron 15:961-973. - PubMed
-
- Azizeh, B. Y., D. H. Cribbs, V. M. Kreng, and C. W. Cotman. 1998. Cross-linking of NCAM receptors on neurons induces programmed cell death. Brain Res. 796:20-26. - PubMed
-
- Beggs, H. E., S. C. Baragona, J. Hemperly, and P. F. Maness. 1997. NCAM140 interacts with the focal adhesion kinase p125(fak) and the SRC-related tyrosine kinase p59(fyn). J. Biol. Chem. 272:8310-8319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
