Analysis of Spt7 function in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SAGA coactivator complex
- PMID: 12101232
- PMCID: PMC133947
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5367-5379.2002
Analysis of Spt7 function in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SAGA coactivator complex
Abstract
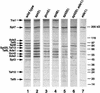
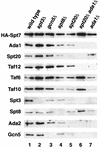
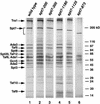
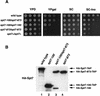
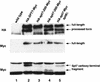
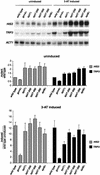
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SAGA complex is required for the normal transcription of a large number of genes. Complex integrity depends on three core subunits, Spt7, Spt20, and Ada1. We have investigated the role of Spt7 in the assembly and function of SAGA. Our results show that Spt7 is important in controlling the levels of the other core subunits and therefore of SAGA. In addition, partial SAGA complexes containing Spt7 can be assembled in the absence of both Spt20 and Ada1. Through biochemical and genetic analyses of a series of spt7 deletion mutants, we have identified a region of Spt7 required for interaction with the SAGA component Spt8. An adjacent Spt7 domain was found to be required for a processed form of Spt7 that is present in a previously identified altered form of SAGA called SLIK, SAGA(alt), or SALSA. Analysis of an spt7 mutant with greatly reduced levels of SLIK/SAGA(alt)/SALSA suggests a subtle role for this complex in transcription that may be redundant with a subset of SAGA functions.
Figures



References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1988. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates/Wiley-Interscience, New York, N.Y.
-
- Balasubramanian, R., M. G. Pray-Grant, W. Selleck, P. A. Grant, and S. Tan. 2001. Role of the Ada2 and Ada3 transcriptional coactivators in histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:7989-7995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
