The UV (Ribotoxic) stress response of human keratinocytes involves the unexpected uncoupling of the Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling cascade from the activated epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 12101233
- PMCID: PMC133934
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5380-5394.2002
The UV (Ribotoxic) stress response of human keratinocytes involves the unexpected uncoupling of the Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling cascade from the activated epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
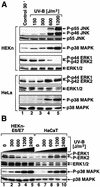
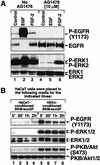
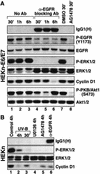
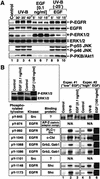
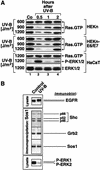
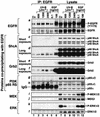
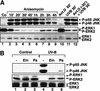
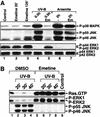
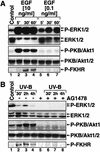
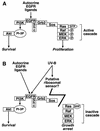
In mammals, UVB radiation is of biological relevance primarily for the cells of the epidermis. We report here the existence of a UVB response that is specific for proliferating human epidermal keratinocytes. Unlike other cell types that also display a UVB response, keratinocytes respond to UVB irradiation with a transient but potent downregulation of the Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling cascade. The downregulation of ERK precedes a profound decrease in the steady-state levels of cyclin D1, a mediator of the proliferative action of ERK. Keratinocytes exhibit high constitutive activity of the Ras-ERK signaling cascade even in culture medium lacking supplemental growth factors. The increased activity of Ras and phosphorylation of ERK in these cells are maintained by the autocrine production of secreted molecules that activate the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Irradiation of keratinocytes increases the phosphorylation of EGFR on tyrosine residues Y845, Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1086, Y1148, and Y1173 above the basal levels and leads to the increased recruitment of the adaptor proteins Grb2 and ShcA and of a p55 form of the regulatory subunit of the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase to the UVB-activated EGFR. Paradoxically, however, UVB causes, at the same time, the inactivation of Ras and a subsequent dephosphorylation of ERK. By contrast, the signaling pathway leading from the activated EGFR to the phosphorylation of PKB/Akt1 is potentiated by UVB. The UVB response of keratinocytes appeared to be a manifestation of the more general ribotoxic stress response inasmuch as the transduction of the UVB-generated inhibitory signal to Ras and ERK required the presence of active ribosomes at the time of irradiation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cholecystokinin stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase through activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Yes, and protein kinase C. Signal amplification at the level of Raf by activation of protein kinase Cepsilon.J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 28;278(9):7065-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211234200. Epub 2002 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12496267
-
Signaling complexes and protein-protein interactions involved in the activation of the Ras and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways by the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 15;275(50):39159-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006908200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10995764
-
Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibits integrin- and growth factor-mediated mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathways.J Cell Biol. 1998 Nov 30;143(5):1375-83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.5.1375. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9832564 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin signalling.J Cell Sci. 2001 Apr;114(Pt 8):1429-30. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.8.1429. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11282018 Review. No abstract available.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor and integrins meet redox signaling through P66shc and Rac1.Cytokine. 2021 Oct;146:155625. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155625. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 34157521 Review.
Cited by
-
Ribosome Collisions Trigger General Stress Responses to Regulate Cell Fate.Cell. 2020 Jul 23;182(2):404-416.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32610081 Free PMC article.
-
Amentoflavone-Enriched Selaginella rossii Protects against Ultraviolet- and Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging in Skin Cells.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;12(12):2106. doi: 10.3390/life12122106. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556471 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of both the epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB2 effectively inhibits the promotion of skin tumors during two-stage carcinogenesis.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010 Aug;3(8):940-52. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0010. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010. PMID: 20682802 Free PMC article.
-
Erbb2 regulates inflammation and proliferation in the skin after ultraviolet irradiation.Am J Pathol. 2006 Oct;169(4):1402-14. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060082. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17003495 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Small GTPase RhoA in DNA Damage Response.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 3;11(2):212. doi: 10.3390/biom11020212. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33546351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albanell, J., J. Codony-Servat, F. Rojo, J. M. Del Campo, S. Sauleda, J. Anido, G. Raspall, J. Giralt, J. Rosello, R. I. Nicholson, J. Mendelsohn, and J. Baselga. 2001. Activated extracellular signal-regulated kinases: association with epidermal growth factor receptor/transforming growth factor alpha expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma and inhibition by anti-epidermal growth factor receptor treatments. Cancer Res. 61:6500-6510. - PubMed
-
- Assoian, R. K., and M. A. Schwartz. 2001. Coordinate signaling by integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases in the regulation of G1 phase cell-cycle progression. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11:48-53. - PubMed
-
- Balmanno, K., and S. J. Cook. 1999. Sustained MAP kinase activation is required for the expression of cyclin D1, p21Cip1 and a subset of AP-1 proteins in CCL39 cells. Oncogene 18:3085-3097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
