NF-kappaB1 can inhibit v-Abl-induced lymphoid transformation by functioning as a negative regulator of cyclin D1 expression
- PMID: 12101248
- PMCID: PMC133951
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.15.5563-5574.2002
NF-kappaB1 can inhibit v-Abl-induced lymphoid transformation by functioning as a negative regulator of cyclin D1 expression
Abstract
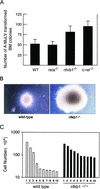
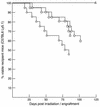
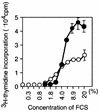
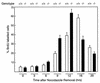
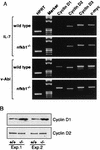
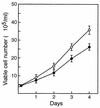
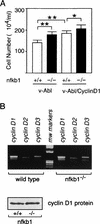
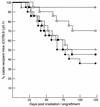
Mounting evidence implicates deregulated Rel/NF-kappaB signaling as a common feature of lymphoid malignancies. Despite the fact that they promote the survival and proliferation of normal lymphocytes, the underlying mechanisms by which various Rel/NF-kappaB proteins with different transcriptional regulatory capacities might facilitate transformation remain to be established. Here we show that the proliferation and tumorigenicity of Abelson murine leukemia virus (A-MuLV)-transformed pre-B cells are enhanced in the absence of NF-kappaB1 and that this coincides with elevated levels of cyclin D1. Support for a link between cyclin D1 expression and v-Abl transformation came from the finding that proliferation of transformed pre-B cells was reduced in the absence of cyclin D1, while enforced cyclin D1 expression increased the proliferation and tumorigenicity of wild-type transformants. A reduction in endogenous cyclin D1 levels that coincided with NF-kappaB1 transgene reversal of enhanced nfkb1(-/-) pre-B-cell transformation, coupled with NF-kappaB1 inhibition of v-Abl-induced kappaB-dependent murine cyclin D1 transcription, lends support to a model in which v-Abl-induced cyclin D1 transcription in transformed pre-B cells is controlled by Rel/NF-kappaB dimers with different activities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Growth, differentiation, and malignant transformation of pre-B cells mediated by inducible activation of v-Abl oncogene.J Immunol. 2006 Jun 1;176(11):6831-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6831. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16709843
-
B lymphocytes differentially use the Rel and nuclear factor kappaB1 (NF-kappaB1) transcription factors to regulate cell cycle progression and apoptosis in quiescent and mitogen-activated cells.J Exp Med. 1998 Mar 2;187(5):663-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.5.663. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9480976 Free PMC article.
-
The v-abl tyrosine kinase negatively regulates NF-kappa B/Rel factors and blocks kappa gene transcription in pre-B lymphocytes.Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 15;8(6):678-87. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.6.678. Genes Dev. 1994. PMID: 7926758
-
NF-kappaB and cell-cycle regulation: the cyclin connection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001 Mar;12(1):73-90. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(00)00018-6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001. PMID: 11312120 Review.
-
Arrested development: understanding v-abl.Bioessays. 1994 Jul;16(7):453-5. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160702. Bioessays. 1994. PMID: 7945272 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced miR-3127-5p expression promotes NSCLC proliferation/invasion and contributes to dasatinib sensitivity via the c-Abl/Ras/ERK pathway.Sci Rep. 2014 Oct 6;4:6527. doi: 10.1038/srep06527. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25284075 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factors c-rel and RelA control epidermal development and homeostasis in embryonic and adult skin via distinct mechanisms.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(13):5733-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.13.5733-5745.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15199130 Free PMC article.
-
NFKB1 as a key player in Tumor biology: from mechanisms to therapeutic implications.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 11;41(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09974-2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39797972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term culture of keratinocyte-like cells derived from mouse embryonic stem cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008 Jul-Aug;44(7):193-203. doi: 10.1007/s11626-008-9092-2. Epub 2008 Jun 5. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008. PMID: 18528735
-
Viral induction of AID is independent of the interferon and the Toll-like receptor signaling pathways but requires NF-kappaB.J Exp Med. 2007 Feb 19;204(2):259-65. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061801. Epub 2007 Jan 22. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17242162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldwin, A. S., Jr. 1996. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649-681. - PubMed
-
- Beg, A. A., W. C. Sha, R. Bronson, S. Ghosh, and D. Baltimore. 1995. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the relA component of NF-κB. Nature 376:167-170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
