Precise control of PLG microsphere size provides enhanced control of drug release rate
- PMID: 12106984
- PMCID: PMC4140625
- DOI: 10.1016/s0168-3659(02)00136-0
Precise control of PLG microsphere size provides enhanced control of drug release rate
Abstract
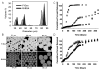
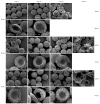
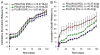
An important limitation in the development of biodegradable polymer microspheres for controlled-release drug delivery applications has been the difficulty of specifically designing systems exhibiting precisely controlled release rates. Because microparticle size is a primary determinant of drug release, we developed a methodology for controlling release kinetics employing monodisperse poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLG) microspheres. We fabricated 20-, 40- and 65-microm diameter rhodamine-containing microspheres and 10-, 50- and 100-microm diameter piroxicam-containing microspheres at various loadings from 1 to 20%. In vitro release kinetics were determined for each preparation. Drug release depended strongly on microsphere diameter with 10- and 20-microm particles exhibiting concave-downward release profiles while larger particles resulted in sigmoidal release profiles. Overall, the rate of release decreased and the duration increased with increasing microsphere size. Release kinetics from mixtures of uniform microspheres corresponded to mass-weighted averages of the individual microsphere release kinetics. Appropriate mixtures of uniform microspheres were identified that provided constant (zero-order) release of rhodamine and piroxicam for 8 and 14 days, respectively. Mixing of uniform microspheres, as well as control of microsphere size distribution, may provide an improved methodology to tailor small-molecule drug-release kinetics from simple, biodegradable-polymer microparticles.
Copyright 2002 Elsevier Science B.V.
Figures










References
-
- Almería B, Deng W, Fahmy TM, Gomez A. Controlling the morphology of electrospray-generated PLGA microparticles for drug delivery. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 2010;343:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JM, Shive MS. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2012;64(Supplement):72–82. - PubMed
-
- Badri Viswanathan N, Patil SS, Pandil JK, Lele AK, Kulkarni MG, Mashelkar RA. Morphological changes in degrading PLGA and P(DL)LA microspheres: implications for the design of controlled release systems. Journal of Microencapsulation. 2001;18:783–800. - PubMed
-
- Batycky RP, Hanes J, Langer R, Edwards DA. A theoretical model of erosion and macromolecular drug release from biodegrading microspheres. Journal of Pharmceutical Sciences. 1997;86:1464–1477. - PubMed
-
- Berkland C. Control of micro- and nano- sphere size distributions: implications in drug delivery, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; Urbana-Champaign: 2003.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

