Molecular profiling of angiogenesis markers
- PMID: 12107087
- PMCID: PMC1850687
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64154-5
Molecular profiling of angiogenesis markers
Abstract
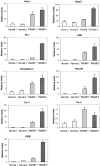
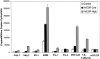
The goal of this study was to develop a sensitive, simple, and widely applicable assay to measure copy numbers of specific mRNAs using real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and identify a profile of gene expression closely associated with angiogenesis. We measured a panel of nine potential angiogenesis markers from a mouse transgenic model of prostate adenocarcinoma (TRAMP) and a mouse skin model of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-driven angiogenesis. In both models, expression of VEGF correlated with expression of mRNAs encoding other angiogenic cytokines (angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2), endothelial cell receptor tyrosine kinases (Flt-1, KDR, Tie-1), and endothelial cell adhesion molecules (VE-cadherin, PECAM-1). Relative to control, in dermis highly stimulated by VEGF, the Ang-2 mRNA transcript numbers increased 35-fold, PECAM-1 and VE-cadherin increased 10-fold, Tie-1 increased 8-fold, KDR and Flt-1 each increased 4-fold, and Ang-1 increased 2-fold. All transcript numbers were correspondingly reduced in skin with less VEGF expression, indicating a relationship of each of these seven markers with VEGF. Thus, this study identifies a highly efficient method for precise quantification of a panel of seven specific mRNAs that correlate with VEGF expression and VEGF-induced neovascularization, and it provides evidence that real-time quantitative RT-PCR offers a highly sensitive strategy for monitoring angiogenesis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Molecular profiling of angiogenic markers: a step towards interpretive analysis of a complex biological function.Am J Pathol. 2002 Jul;161(1):7-11. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64150-8. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12107083 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Folkman J: What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 1990, 82:4-6 - PubMed
-
- Folkman J, D’Amore PA: Blood vessel formation: what is its molecular basis? Cell 1996, 87:1153-1155 - PubMed
-
- Stetler-Stevenson WG: The role of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Surg Oncol Clin North Am 2001, 10:383-392 - PubMed
-
- Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM: Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res 1996, 6:986-994 - PubMed
-
- Jung R, Soondrum K, Neumaier M: Quantitative PCR. Clin Chem Lab Med 2000, 38:833-836 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

