Autoantibodies to type VII collagen mediate Fcgamma-dependent neutrophil activation and induce dermal-epidermal separation in cryosections of human skin
- PMID: 12107115
- PMCID: PMC1850704
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64182-x
Autoantibodies to type VII collagen mediate Fcgamma-dependent neutrophil activation and induce dermal-epidermal separation in cryosections of human skin
Abstract
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita is an autoimmune subepidermal blistering disease associated with autoantibodies to type VII collagen, the major constituent of anchoring fibrils. Previous attempts to demonstrate the blister-inducing potential of autoantibodies to this protein have failed. To address this question, we used an in vitro model involving cryosections of human skin incubated with patients' autoantibodies and leukocytes from healthy donors. We show that sera from 14 of 16 epidermolysis bullosa acquisita patients, in contrast to sera from healthy controls, induced dermal-epidermal separation in the cryosections. Recruitment and activation of neutrophils at the dermal-epidermal junction was necessary for split induction, whereas mononuclear cells were not required. Importantly, patients' autoantibodies affinity-purified against a recombinant form of the noncollagenous 1 domain of type VII collagen retained their blister-inducing capacity in a dose-dependent manner, whereas patients' IgG that was depleted of reactivity to type VII collagen lost this ability. Monoclonal antibody LH7.2 to the noncollagenous 1 domain of type VII collagen also induced subepidermal splits in the cryosections; F(ab')(2) fragments of autoantibodies to type VII collagen were not pathogenic. We demonstrate the capacity of autoantibodies to type VII collagen to trigger an Fcgamma-dependent inflammation leading to split formation in cryosections of human skin.
Figures
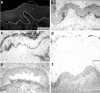
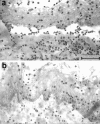
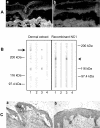
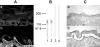


References
-
- Woodley DT, Gammon WR, Briggaman RA: Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita 1999. Freedberg IM Eisen AZ Wolff K Austen KF Goldsmith LA Katz SI Fitzpatrick TB eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine, ed 4 1999:pp 702-709 McGraw-Hill, New York
-
- Gammon WR, Briggaman RA, Inman AOD, Queen LL, Wheeler CE: Differentiating anti-lamina lucida and anti-sublamina densa anti-BMZ antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence on 1.0 M sodium chloride-separated skin. J Invest Dermatol 1984, 82:139-144 - PubMed
-
- Yaoita H, Briggaman RA, Lawley TJ, Provost TT, Katz SI: Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: ultrastructural and immunological studies. J Invest Dermatol 1981, 76:288-292 - PubMed
-
- Woodley DT, Briggaman RA, O’Keefe EJ, Inman AO, Queen LL, Gammon WR: Identification of the skin basement-membrane autoantigen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. N Engl J Med 1984, 310:1007-1013 - PubMed
-
- Shimizu H, Ishiko A, Masunaga T, Kurihara Y, Sato M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Nishikawa T: Most anchoring fibrils in human skin originate and terminate in the lamina densa. Lab Invest 1997, 76:753-763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

