How does infliximab work in rheumatoid arthritis?
- PMID: 12110154
- PMCID: PMC3238217
- DOI: 10.1186/ar549
How does infliximab work in rheumatoid arthritis?
Abstract
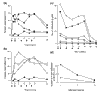
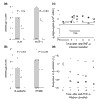
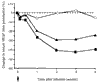
Since the initial characterization of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha), it has become clear that TNFalpha has diverse biologic activity. The realization that TNFalpha plays a role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has led to the development of anti-TNF agents for the treatment of RA. Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody that specifically, and with high affinity, binds to TNFalpha and neutralizes the cytokine, is currently approved for the treatment of RA and Crohn's disease, another immune-inflammatory disorder. In addition to establishing the safety and efficacy of infliximab, clinical research has also provided insights into the complex cellular and cytokine-dependent pathways involved in the pathophysiology of RA, including evidence that supports TNFalpha involvement in cytokine regulation, cell recruitment, angiogenesis, and tissue destruction.
Figures
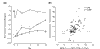


References
-
- Maini RN, Feldmann M. , Eds. Pocket Reference to TNFα Antagonism and Rheumatoid Arthritis. London: Science Press, Ltd; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

