Dissolution of the maskin-eIF4E complex by cytoplasmic polyadenylation and poly(A)-binding protein controls cyclin B1 mRNA translation and oocyte maturation
- PMID: 12110596
- PMCID: PMC126103
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf353
Dissolution of the maskin-eIF4E complex by cytoplasmic polyadenylation and poly(A)-binding protein controls cyclin B1 mRNA translation and oocyte maturation
Abstract
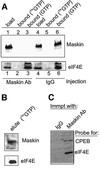
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation stimulates the translation of several dormant mRNAs during oocyte maturation in Xenopus. Polyadenylation is regulated by the cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE), a cis-acting element in the 3'-untranslated region of responding mRNAs, and its associated factor CPEB. CPEB also binds maskin, a protein that in turn interacts with eIF4E, the cap-binding factor. Here, we report that based on antibody and mRNA reporter injection assays, maskin prevents oocyte maturation and the translation of the CPE-containing cyclin B1 mRNA by blocking the association of eIF4G with eIF4E. Dissociation of the maskin-eIF4E complex is essential for cyclin B1 mRNA translational activation, and requires not only cytoplasmic polyadenylation, but also the poly(A)-binding protein. These results suggest a molecular mechanism by which CPE- containing mRNA is activated in early development.
Figures



References
-
- Bilger A., Fox,C.A., Wahle,E. and Wickens,M. (1994) Nuclear poly adenylation factors recognize cytoplasmic polyadenylation elements. Genes Dev., 8, 1106–1116. - PubMed
-
- Cornelis S., Bruynooghe,Y., Denecker,G., Van Huffel,S., Tinton,S. and Beyaert,R. (2000) Identification and characterization of a novel cell cycle-regulated internal ribosome entry site. Mol. Cell, 5, 597–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

