Structure and mechanism of T4 polynucleotide kinase: an RNA repair enzyme
- PMID: 12110598
- PMCID: PMC126130
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf397
Structure and mechanism of T4 polynucleotide kinase: an RNA repair enzyme
Abstract
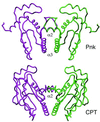
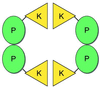
T4 polynucleotide kinase (Pnk), in addition to being an invaluable research tool, exemplifies a family of bifunctional enzymes with 5'-kinase and 3'-phosphatase activities that play key roles in RNA and DNA repair. T4 Pnk is a homotetramer composed of a C-terminal phosphatase domain and an N-terminal kinase domain. The 2.0 A crystal structure of the isolated kinase domain highlights a tunnel-like active site through the heart of the enzyme, with an entrance on the 5' OH acceptor side that can accommodate a single-stranded polynucleotide. The active site is composed of essential side chains that coordinate the beta phosphate of the NTP donor and the 3' phosphate of the 5' OH acceptor, plus a putative general acid that activates the 5' OH. The structure rationalizes the different specificities of T4 and eukaryotic Pnk and suggests a model for the assembly of the tetramer.
Figures

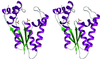


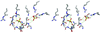
Similar articles
-
Structure of a tRNA repair enzyme and molecular biology workhorse: T4 polynucleotide kinase.Structure. 2002 Sep;10(9):1249-60. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00835-3. Structure. 2002. PMID: 12220496
-
Domain structure and mutational analysis of T4 polynucleotide kinase.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 20;276(29):26868-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103663200. Epub 2001 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11335730
-
Structure-function analysis of the 3' phosphatase component of T4 polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase.Virology. 2007 Sep 15;366(1):126-36. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.03.059. Epub 2007 May 9. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17493655 Free PMC article.
-
Polynucleotide kinase as a potential target for enhancing cytotoxicity by ionizing radiation and topoisomerase I inhibitors.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008 May;8(4):358-67. doi: 10.2174/187152008784220311. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18473721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of linker-scanning mutations by oligonucleotide ligation.Methods Mol Biol. 1996;57:279-85. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-332-5:279. Methods Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8850014 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of RNA 2',3'-cyclic phosphate end healing by T4 polynucleotide kinase-phosphatase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan 7;41(1):355-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks977. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23118482 Free PMC article.
-
The essential function of the Trypanosoma brucei Trl1 homolog in procyclic cells is maturation of the intron-containing tRNATyr.RNA. 2016 Aug;22(8):1190-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.056242.116. Epub 2016 Jun 9. RNA. 2016. PMID: 27284166 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and roles of (t)RNA ligases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(16):2657-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0944-2. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22426497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-function analysis of the kinase-CPD domain of yeast tRNA ligase (Trl1) and requirements for complementation of tRNA splicing by a plant Trl1 homolog.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 20;34(2):517-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj441. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16428247 Free PMC article.
-
Two-step mechanism and step-arrest mutants of Runella slithyformis NAD+-dependent tRNA 2'-phosphotransferase Tpt1.RNA. 2018 Sep;24(9):1144-1157. doi: 10.1261/rna.067165.118. Epub 2018 Jun 8. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29884622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abelson J., Trotta,C.R. and Li,H. (1998) tRNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 12685–12688. - PubMed
-
- Becker A. and Hurwitz,J. (1967) The enzymatic cleavage of phosphate termini from polynucleotides. J. Biol. Chem., 242, 936–950. - PubMed
-
- Berry M.B. and Phillips,G.N. (1998) Crystal structures of Bacillus stearothermophilus adenylate kinase with bound Ap5A, Mg2+ Ap5A, and Mn2+ Ap5A reveal an intermediate lid position and six coordinate octahedral geometry for bound Mg2+ and Mn2+. Proteins, 32, 276–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

