Investigation of neurotransmission in vas deferens from alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptor knockout mice
- PMID: 12110610
- PMCID: PMC1573420
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704791
Investigation of neurotransmission in vas deferens from alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptor knockout mice
Abstract
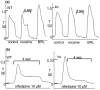
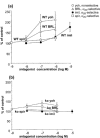
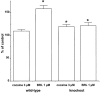
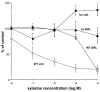
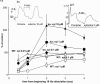
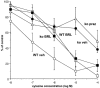
1. We have investigated pre- and post-junctional responsiveness in vas deferens from wild-type and alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptor knockout mice. The response to a single stimulus was not significantly different between wild-type and knock-out mice. The isometric contraction to 10 Hz stimulation for 4 s was significantly larger in vas deferens from knockout as compared with wild-type. 2. The maximum potentiation of 10 Hz stimulation-evoked contractions by yohimbine was to 206.2+/-38.0% of control in wild-type but to 135.8+/-13.6% of control in knockout. The alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptor selective antagonist BRL 44408 significantly increased the 10 Hz stimulation-evoked contraction in wild-type but not knockout, and the reverse was true for the alpha(2C)-adrenoceptor selective antagonist spiroxatrine. The alpha(2B)-adrenoceptor antagonist imiloxan had no effect on the evoked contraction except at high concentrations, and only in wild-type. Following cocaine (3 microM) and BRL 44408 (1 microM), 10 Hz responses were similar in shape and maximum between wild-type and knock-out. 3. The alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonist xylazine virtually abolished the early component of the contraction to 10 Hz stimulation in the presence of nifedipine (10 microM) in vas deferens from knockout mice in a way consistent with a change of receptor subtype but without clear evidence for a reduced receptor number. However, the late component of the contraction to 10 Hz stimulation was significantly potentiated by xylazine in tissues from knock-out mice. 4. It is concluded that, although non-alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptors replace alpha(2D)-adrenoceptors in this knockout, the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonist and antagonist data are contradictory. The antagonist data suggest a major loss of prejunctional alpha(2)-adrenoceptors, but this is not necessarily supported by the agonist data.
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 136, 857-864
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of postjunctional alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes in vas deferens from wild-type and alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptor knockout mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;138(6):1069-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705137. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12684262 Free PMC article.
-
Prejunctional actions of methylenedioxymethamphetamine in vas deferens from wild-type and alpha(2A/D)-adrenoceptor knockout mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Jul 6;423(2-3):223-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01118-9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11448488
-
Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8098642 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes.Pharmacol Res. 2001 Sep;44(3):195-208. doi: 10.1006/phrs.2001.0857. Pharmacol Res. 2001. PMID: 11529686 Review.
-
Ageing and alpha-adrenoceptors.Clin Sci (Lond). 1985;68 Suppl 10:133s-136s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s133. Clin Sci (Lond). 1985. PMID: 2857609 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of monoamines in the changes in body temperature induced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) and its derivatives.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;160(5):1029-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00722.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles for α1-adrenoceptors during contractions by electrical field stimulation in mouse vas deferens.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 1;25(6):525-532. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.6.525. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34697263 Free PMC article.
-
Role of alpha2A-adrenoceptors in the effects of MDMA on body temperature in the mouse.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Sep;146(1):1-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706320. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16025144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALTMAN J.D., TRENDELENBURG A.U., MACMILLAN L., BERNSTEIN D., LIMBIRD L., STARKE K., KOBILKA B.K., HEIN L. Abnormal regulation of the sympathetic nervous system in α2A-adrenoceptor knockout mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999;56:154–161. - PubMed
-
- BULTMANN R., VON KUGELGEN I., STARKE K. Contraction-mediating α2-adrenoceptors in the mouse vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1991;343:623–632. - PubMed
-
- BYLUND D.B. Subtypes of α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors. FASEB J. 1992;6:832–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

