Potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions of a novel thymulin-related peptide in the rat
- PMID: 12110619
- PMCID: PMC1573422
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704793
Potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions of a novel thymulin-related peptide in the rat
Abstract
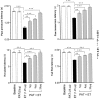
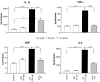
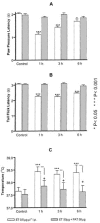
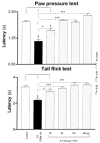
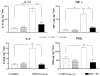
1. The present study examines the effect of PAT (peptide analogue of thymulin) in two rat models of inflammatory hyperalgesia induced by either i.pl. (1.25 microg in 50 microl saline) or i.p. (50 microg in 100 microl) injections of endotoxin ET. 2. Pretreatment with PAT (1, 5 or 25 microg in 100 microl saline, i.p.) decreased, in a dose dependent manner, both mechanical hyperalgesia, determined by the paw pressure (PP) test and thermal hyperalgesia determined by the hot plate (HP), the paw immersion (PI) and the tail flick (TF) tests. 3. Compared to the tripeptides K(D)PT and K(D)PV, known to antagonize interleukin (IL)-1beta or IL-1beta and PGE(2) mechanisms, PAT, at lower dosages, exerted stronger anti-hyperalgesic effects. 4. When compared with the effect of a steroidal (dexamethasone) and a non-steroidal (indomethacin) anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), PAT demonstrated equal analgesic actions. 5. Pretreatment with PAT, reduced significantly the increased concentration of IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha and NGF due to i.pl. injection of ET. 6. Injection of i.p. ET produced sickness behaviour characterized by hyperalgesia and fever. Pretreatment with PAT prevented the hyperalgesia and maintained the body temperature within the normal range and was accompanied by a down-regulation of the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and PGE(2) in the liver. 7. PAT, in all doses used, did not result in any evident changes in the physiological parameters or in the normal behaviour of the rats. 8. The anti-hyperalgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of PAT can be attributed, at least partially, to the down-regulation of pro-inflammatory mediators.
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002) 136, 947-955
Figures

References
-
- BARNES P.J., ADCOCK I. Antiinflammatory actions of steroids: molecular mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1993;14:436–441. - PubMed
-
- BENEDETTI C., BUTLER S.H.Systemic analgesics Management of Pain 1990Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger; 1640–1675.ed. Bonica, J.J
-
- BORCHARD R.E., BARNES C.D., ELTHERINGTON L.G. Drug dosage in laboratory animals. 1992Florida: Boca Raton; A handbook, 3rd edn
-
- CAMUSSI G., LUPIA E. The future of anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) products in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs. 1998;55:613–620. - PubMed
-
- CAO C., MATSUMURA K., YAMAGATA K., WATANABE Y. Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 in LPS-induced fever and regulation of its mRNA by LPS in the rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;272:R1712–R1725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

