Comparison of spatial normalization procedures and their impact on functional maps
- PMID: 12112765
- PMCID: PMC6871934
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.10047
Comparison of spatial normalization procedures and their impact on functional maps
Abstract
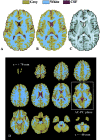
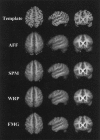
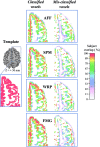
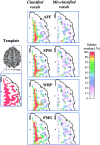
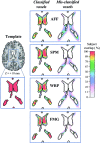
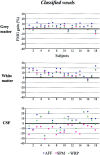
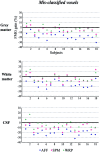
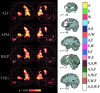
The alignment accuracy and impact on functional maps of four spatial normalization procedures have been compared using a set of high resolution brain MRIs and functional PET volumes acquired in 20 subjects. Simple affine (AFF), fifth order polynomial warp (WRP), discrete cosine basis functions (SPM), and a movement model based on full multi grid (FMG) approaches were applied on the same dataset for warping individual volumes onto the Human Brain Atlas (HBA) template. Intersubject averaged structural volumes and tissue probability maps were compared across normalization methods and to the standard brain. Thanks to the large number of degrees of freedom of the technique, FMG was found to provide enhanced alignment accuracy as compared to the other three methods, both for the grey and white matter tissues; WRP and SPM exhibited very similar performances whereas AFF had the lowest registration accuracy. SPM, however, was found to perform better than the other methods for the intra-cerebral cerebrospinal fluid (mainly in the ventricular compartments). Limited differences in terms of activation morphology and detection sensitivity were found between low resolution functional maps (FWHM approximately 10 mm) spatially normalized with the four methods, which overlapped in 42.8% of the total activation volume. These findings suggest that the functional variability is much larger than the anatomical one and that precise alignment of anatomical features has low influence on the resulting intersubject functional maps. When increasing the spatial resolution to approximately 6 mm, however, differences in localization of activated areas appear as a consequence of the different spatial normalization procedure used, restricting the overlap of the normalized activated volumes to only 6.2%.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Abell F, Krams M, Ashburner J, Passingham RE, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RSJ, Happé F, Frith CD, Frith U (1999): The neuroanatomy of autism: a voxel‐based whole brain analysis of structural scans. Neuroreport 10: 1647–1651. - PubMed
-
- Amunts K, Schleicher A, Bürgel U, Mohlberg H, Uylings H, Zilles K (1999): Broca region revisited: cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. J Comp Neurol 412: 319–341. - PubMed
-
- Andersson JLR, Thurfjell L (1997): Implementation and validation of a fully automatic system for intra‐ and interindividual registration of PET brain scans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21: 136–144. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ (1997): Multimodal image coregistration and partitioning: a unified framework. Neuroimage 6: 209–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

