mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK
- PMID: 12114539
- PMCID: PMC126623
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152327199
mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK
Abstract
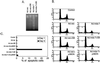
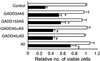
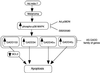
Subtraction hybridization identified melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 (mda-7) as a gene induced during terminal differentiation in human melanoma cells. On the basis of structure, chromosomal localization and cytokine-like properties, mda-7 is classified as IL-24. Administration of mda-7/IL-24 by means of a replication-incompetent adenovirus (Ad.mda-7) induces apoptosis selectively in diverse human cancer cells without inducing harmful effects in normal fibroblast or epithelial cells. The present studies investigated the mechanism underlying this differential apoptotic effect. Infection of melanoma cells, but not normal immortal melanocytes, with Ad.mda-7 induced a time- and dose-dependent increase in expression, mRNA and protein, of a family of growth arrest and DNA damage (GADD)-inducible genes, which correlated with induction of apoptosis. Among the members of the GADD family of genes, GADD153, GADD45 alpha, and GADD34 displayed marked, and GADD45 gamma showed minimal induction. Treatment of melanoma cells with SB203580, a selective inhibitor of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, effectively inhibited Ad.mda-7-induced apoptosis. Additional support for an involvement of the p38 MAPK pathway in Ad.mda-7-mediated apoptosis was documented by using an adenovirus expressing a dominant negative mutant of p38 MAPK. Infection with Ad.mda-7 increased the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and heat shock protein 27 in melanoma cells but not in normal immortal melanocytes. In addition, SB203580 effectively inhibited Ad.mda-7-mediated induction of the GADD family of genes in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and it effectively blocked Ad.mda-7-mediated down-regulation of the antiapoptotic protein BCL-2. Inhibition of GADD genes by an antisense approach either alone or in combination also effectively blocked Ad.mda-7-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells. These results support the hypothesis that Ad.mda-7 mediates induction of the GADD family of genes by means of the p38 MAPK pathway, thereby resulting in the selective induction of apoptosis in human melanoma cells.
Figures



References
-
- Sachs L. Nature (London) 1978;274:535–539. - PubMed
-
- Fisher P B, Grant S. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;27:143–166. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Lin J, Fisher P B. Mol Cell Differ. 1994;2:221–239.
-
- Leszczyniecka M, Roberts T, Dent P, Grant S, Fisher P B. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;90:105–156. - PubMed
-
- Waxman S. Differentiation Therapy. Rome: Ares-Serono Symposia Publishers; 1996. pp. 1–531.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

