Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, an enzyme involved in processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol
- PMID: 12114544
- PMCID: PMC124980
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152333599
Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, an enzyme involved in processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol
Abstract
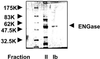
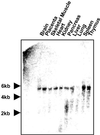
Formation of oligosaccharides occurs both in the cytosol and in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Luminal oligosaccharides are transported into the cytosol to ensure that they do not interfere with proper functioning of the glycan-dependent quality control machinery in the lumen of the ER for newly synthesized glycoproteins. Once in the cytosol, free oligosaccharides are catabolized, possibly to maximize the reutilization of the component sugars. An endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENGase) is a key enzyme involved in the processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol. This enzyme activity has been widely described in animal cells, but the gene encoding this enzyme activity has not been reported. Here, we report the identification of the gene encoding human cytosolic ENGase. After 11 steps, the enzyme was purified 150,000-fold to homogeneity from hen oviduct, and several internal amino acid sequences were analyzed. Based on the internal sequence and examination of expressed sequence tag (EST) databases, we identified the human orthologue of the purified protein. The human protein consists of 743 aa and has no apparent signal sequence, supporting the idea that this enzyme is localized in the cytosol. By expressing the cDNA of the putative human ENGase in COS-7 cells, the enzyme activity in the soluble fraction was enhanced 100-fold over the basal level, confirming that the human gene identified indeed encodes for ENGase. Careful gene database surveys revealed the occurrence of ENGase homologues in Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Arabidopsis thaliana, indicating the broad occurrence of ENGase in higher eukaryotes. This gene was expressed in a variety of human tissues, suggesting that this enzyme is involved in basic biological processes in eukaryotic cells.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

