Methyl jasmonate induces traumatic resin ducts, terpenoid resin biosynthesis, and terpenoid accumulation in developing xylem of Norway spruce stems
- PMID: 12114556
- PMCID: PMC166496
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.011001
Methyl jasmonate induces traumatic resin ducts, terpenoid resin biosynthesis, and terpenoid accumulation in developing xylem of Norway spruce stems
Abstract
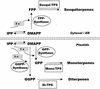
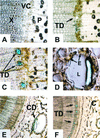
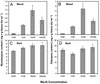
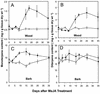
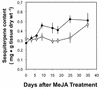
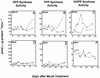
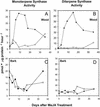
Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst) produces an oleoresin characterized by a diverse array of terpenoids, monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, and diterpene resin acids that can protect conifers against potential herbivores and pathogens. Oleoresin accumulates constitutively in resin ducts in the cortex and phloem (bark) of Norway spruce stems. De novo formation of traumatic resin ducts (TDs) is observed in the developing secondary xylem (wood) after insect attack, fungal elicitation, and mechanical wounding. Here, we characterize the methyl jasmonate-induced formation of TDs in Norway spruce by microscopy, chemical analyses of resin composition, and assays of terpenoid biosynthetic enzymes. The response involves tissue-specific differentiation of TDs, terpenoid accumulation, and induction of enzyme activities of both prenyltransferases and terpene synthases in the developing xylem, a tissue that constitutively lacks axial resin ducts in spruce. The induction of a complex defense response in Norway spruce by methyl jasmonate application provides new avenues to evaluate the role of resin defenses for protection of conifers against destructive pests such as white pine weevils (Pissodes strobi), bark beetles (Coleoptera, Scolytidae), and insect-associated tree pathogens.
Figures

References
-
- Alfaro RI. An induced defense reaction in white spruce to attack by the white pine weevil, Pissodes strobi. Can J For Res. 1995;25:1725–1730.
-
- Alonso WR, Croteau R. Prenyltransferases and cyclases. Methods Plant Biochem. 1993;9:239–260.
-
- Baldwin IT. The jasmonate cascade and the complexity of the induced defense against herbivore attack. Ann Plant Rev. 1999;3:155–186.
-
- Bannan MW. Vertical resin ducts in the secondary wood of the abietineae. New Phytol. 1936;35:11–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

