Glyphosate-resistant goosegrass. Identification of a mutation in the target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase
- PMID: 12114580
- PMCID: PMC166520
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.001560
Glyphosate-resistant goosegrass. Identification of a mutation in the target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase
Abstract
The spontaneous occurrence of resistance to the herbicide glyphosate in weed species has been an extremely infrequent event, despite over 20 years of extensive use. Recently, a glyphosate-resistant biotype of goosegrass (Eleusine indica) was identified in Malaysia exhibiting an LD(50) value approximately 2- to 4-fold greater than the sensitive biotype collected from the same region. A comparison of the inhibition of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) activity by glyphosate in extracts prepared from the resistant (R) and sensitive (S) biotypes revealed an approximately 5-fold higher IC(50)(glyphosate) for the (R) biotype. Sequence comparisons of the predicted EPSPS mature protein coding regions from both biotypes revealed four single-nucleotide differences, two of which result in amino acid changes. One of these changes, a proline to serine substitution at position 106 in the (R) biotype, corresponds to a substitution previously identified in a glyphosate-insensitive EPSPS enzyme from Salmonella typhimurium. Kinetic data generated for the recombinant enzymes suggests that the second substitution identified in the (R) EPSPS does not contribute significantly to its reduced glyphosate sensitivity. Escherichia coli aroA- (EPSPS deficient) strains expressing the mature EPSPS enzyme from the (R) biotype exhibited an approximately 3-fold increase in glyphosate tolerance relative to strains expressing the mature EPSPS from the (S) biotype. These results provide the first evidence for an altered EPSPS enzyme as an underlying component of evolved glyphosate resistance in any plant species.
Figures

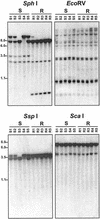



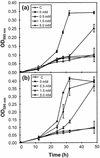
References
-
- Baerson SR, Tran M, Rodriguez DJ, Gonzalez KA, Schafer DE, Krupa DM, Gruys KJ, Stalker DM, Taylor NA, Dill GM. Proceedings, 10th International Conference on Arabidopsis Research. Melrose Park, Australia: Manning Printers PTY LTD; 1999. Comparison of frequencies of individuals resistant to imazethapyr, chlorsulfuron, and glyphosate in EMS-mutagenized populations of Arabidopsis thaliana (cv. Col-0) pp. 5–7.
-
- Benbrook C. Racing against the clock. Agrichem Age. 1991;35:30–33.
-
- Boocock MR, Coggins JR. Kinetics of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase inhibition by glyphosate. FEBS Lett. 1983;154:127–133. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw LD, Padgette SR, Kimball SL, Wells BH. Perspectives on glyphosate resistance. Weed Technol. 1997;11:189–198.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

