Role of nitric oxide in the gastric accommodation reflex and in meal induced satiety in humans
- PMID: 12117883
- PMCID: PMC1773301
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.51.2.219
Role of nitric oxide in the gastric accommodation reflex and in meal induced satiety in humans
Abstract
Aims: In humans, impaired gastric accommodation is associated with early satiety and weight loss. In animals, accommodation involves activation of gastric nitrergic neurones. Our aim was to study involvement of nitric oxide in gastric accommodation and in meal induced satiety in humans.
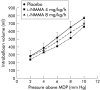
Methods: The effect of N(G)-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) 4 mg/kg/h and 8 mg/kg/h on gastric compliance, on sensitivity to distension, and on gastric accommodation was studied with a barostat in double blind, randomised, placebo controlled studies. The effect of L-NMMA 8 mg/kg/h on meal induced satiety was studied using a drinking test.
Results: L-NMMA had no significant effect on fasting compliance and sensitivity. Ingestion of a meal induced a relaxation of 274 (15) ml which was significantly smaller after L-NMMA 4 mg/kg/h (132 (45) ml; p=0.03) or L-NMMA 8 mg/kg/h (82 (72) ml; p=0.03). L-NMMA 8 mg/kg/h significantly decreased the amount of food ingested at maximum satiety from 1058 (67) to 892 (73) kcal (p<0.01).
Conclusion: In humans, fasting gastric tone and sensitivity to distension are not influenced by nitric oxide synthase inhibition, but the gastric accommodation reflex involves activation of nitrergic neurones. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase impairs accommodation and enhances meal induced satiety.
Figures


References
-
- Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR. Vagally mediated gastric relaxation induced by intestinal nutrients in the dog. Am J Physiol 1986;251:G727–35. - PubMed
-
- Grider JR, Cable MB, Said SI, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide as a neural mediator of gastric relaxation. Am J Physiol 1985;248: G73–8. - PubMed
-
- Li C, Rand M. Nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediate non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory transmission to smooth muscle of the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol 1990;4:303–9. - PubMed
-
- Boeckxstaens G, Pelckmans P, Bogers J, et al. Release of nitric oxide upon stimulation of nonadrenergic noncholinergic nerves in the rat gastric fundus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1991;256:441–7. - PubMed
-
- Boeckxstaens GE, Pelckmans PA, De Man JG, et al. Evidence for a differential release of nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide by non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerves in the rat gastric fundus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1992;318:107–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
