Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi live vector vaccines delivered intranasally elicit regional and systemic specific CD8+ major histocompatibility class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 12117906
- PMCID: PMC128131
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4009-4018.2002
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi live vector vaccines delivered intranasally elicit regional and systemic specific CD8+ major histocompatibility class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
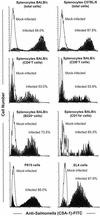
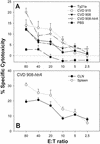
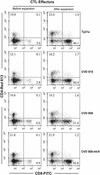
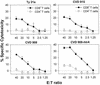
We investigated the ability of live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strains delivered to mice intranasally to induce specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses at regional and systemic levels. Mice immunized with two doses (28 days apart) of Salmonella serovar Typhi strain Ty21a, the licensed oral typhoid vaccine, and genetically attenuated mutants CVD 908 (DeltaaroC DeltaaroD), CVD 915 (DeltaguaBA), and CVD 908-htrA (DeltaaroC DeltaaroD DeltahtrA) induced CTL specific for Salmonella serovar Typhi-infected cells in spleens and cervical lymph nodes. CTL were detected in effector T cells that had been expanded in vitro for 7 days in the presence of Salmonella-infected syngeneic splenocytes. A second round of stimulation further enhanced the levels of specific cytotoxicity. CTL activity was observed in sorted alphabeta+ CD8+ T cells, which were remarkably increased after expansion, but not in CD4+ T cells. CTL from both cervical lymph nodes and spleens failed to recognize Salmonella-infected major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-mismatched cells, indicating that the responses were MHC restricted. Studies in which MHC blocking antibodies were used showed that H-2L(d) was the restriction element. This is the first demonstration that Salmonella serovar Typhi vaccines delivered intranasally elicit CD8+ MHC class I-restricted CTL. The results further support the usefulness of the murine intranasal model for evaluating the immunogenicity of typhoid vaccine candidates at the preclinical level.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Ty21a expressing human papillomavirus type 16 L1 as a potential live vaccine against cervical cancer and typhoid fever.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Oct;14(10):1285-95. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00164-07. Epub 2007 Aug 8. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17687110 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of CD8(+) effector T cell responses in volunteers immunized with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain Ty21a typhoid vaccine.J Immunol. 2002 Aug 15;169(4):2196-203. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.4.2196. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12165550
-
Concomitant induction of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in volunteers immunized with Salmonella enterica serovar typhi strain CVD 908-htrA.J Immunol. 2003 Mar 1;170(5):2734-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.5.2734. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12594304 Clinical Trial.
-
Cell-mediated immunity and antibody responses elicited by attenuated Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi strains used as live oral vaccines in humans.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jul 15;45 Suppl 1:S15-9. doi: 10.1086/518140. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17582562 Review.
-
Host-Salmonella interaction: human trials.Microbes Infect. 2001 Nov-Dec;3(14-15):1271-9. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01487-3. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11755415 Review.
Cited by
-
Presence of wild-type and attenuated Salmonella enterica strains in brain tissues following inoculation of mice by different routes.Infect Immun. 2008 Jul;76(7):3268-72. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00244-08. Epub 2008 May 12. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18474649 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the dynamics of salmonella specific T cell responses.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;334:179-98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-93864-4_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19521686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H2-M3 major histocompatibility complex class Ib-restricted CD8 T cells induced by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection recognize proteins released by Salmonella serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2005 Dec;73(12):8002-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8002-8008.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16299293 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of the endogenous Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi clyA-encoded hemolysin for antigen export enhances the immunogenicity of anthrax protective antigen domain 4 expressed by the attenuated live-vector vaccine strain CVD 908-htrA.Infect Immun. 2004 Dec;72(12):7096-106. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.12.7096-7106.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15557633 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium as a vaccine vector for HIV-1 Gag.Viruses. 2013 Aug 28;5(9):2062-78. doi: 10.3390/v5092062. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23989890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apostolopoulos, V., S. A. Lofthouse, V. Popovski, G. Chelvanayagam, M. S. Sandrin, and I. F. McKenzie. 1998. Peptide mimics of a tumor antigen induce functional cytotoxic T cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 16:276-280. - PubMed
-
- Catic, A., G. Dietrich, I. Gentschev, W. Goebel, S. H. Kaufmann, and J. Hess. 1999. Introduction of protein or DNA delivered via recombinant Salmonella typhimurium into the major histocompatibility complex class I presentation pathway of macrophages. Microbes Infect. 1:113-121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

