Phosphoantigen presentation by macrophages to mycobacterium tuberculosis--reactive Vgamma9Vdelta2+ T cells: modulation by chloroquine
- PMID: 12117907
- PMCID: PMC128132
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4019-4027.2002
Phosphoantigen presentation by macrophages to mycobacterium tuberculosis--reactive Vgamma9Vdelta2+ T cells: modulation by chloroquine
Abstract
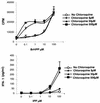
Vgamma9Vdelta2+ T cells (gammadelta T cells) are activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and recognize mycobacterial nonpeptide phosphoantigens. The role of antigen-presenting cells in the processing and presentation of phosphoantigens to Vgamma9Vdelta2+ T cells is not understood. We analyzed the role of macrophages for activation of gammadelta T cells by a new synthetic phosphoantigen bromohydrin pyrophosphate (BrHPP) and M. tuberculosis. Macrophages greatly increased gammadelta T-cell activation by both BrHPP and M. tuberculosis. Fixation of macrophages before infection demonstrated that uptake of M. tuberculosis was required for presentation to gammadelta T cells. Antigens of M. tuberculosis remained stably associated with macrophage surface and were not removed by paraformaldehyde fixation or washing. Macrophages processed M. tuberculosis for gammadelta T cells through a brefeldin A-insensitive pathway, suggesting that transport through the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex of a putative presenting molecule is not important in the early processing of M. tuberculosis antigens for gammadelta T cells. Processing of M. tuberculosis was not eliminated by chloroquine, indicating that processing of gammadelta antigens is not dependent on acidic pH in the lysosomes. Chloroquine treatment of BrHPP-pulsed macrophages increased activation of gammadelta T cells. Ammonium chloride treatment of macrophages did not increase reactivity of gammadelta T cells to BrHPP, indicating that the effect of chloroquine was independent of pH changes in endosomes. Chloroquine, by inhibiting membrane traffic, may increase association and retention of phosphoantigens with cell surface membrane molecules on macrophages.
Figures



References
-
- Ab, B. K., R. Kiessling, J. D. Van Embden, J. E. Thole, D. S. Kumararatne, P. Pisa, A. Wondimu, and T. H. Ottenhoff. 1990. Induction of antigen-specific CD4+ HLA-DR-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes as well as nonspecific nonrestricted killer cells by the recombinant mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein. Eur. J. Immunol. 20:369-377. - PubMed
-
- Adorini, L., S. J. Ullrich, E. Appella, and S. Fuchs. 1990. Inhibition by brefeldin A of presentation of exogenous protein antigens to MHC class II-restricted T cells. Nature 346:63-66. - PubMed
-
- Allison, T. J., C. C. Winter, J. J. Fournie, M. Bonneville, and D. N. Garboczi. 2001. Structure of a human γδ T-cell antigen receptor. Nature 411:820-824. - PubMed
-
- Balaji, K. N., S. K. Schwander, E. A. Rich, and W. H. Boom. 1995. Alveolar macrophages as accessory cells for human γδ T cells activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Immunol. 154:5959-5968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

