Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein- and CD14-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 by lipopolysaccharide in human neutrophils is associated with priming of respiratory burst
- PMID: 12117913
- PMCID: PMC128158
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4068-4074.2002
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein- and CD14-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 by lipopolysaccharide in human neutrophils is associated with priming of respiratory burst
Abstract
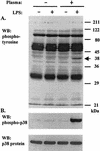
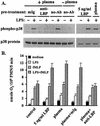
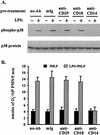
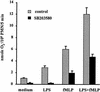
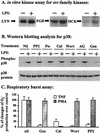
Neutrophil (PMN) functions can be primed for greatly increased oxidative radical release by exposure to certain agents such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Although a variety of signaling pathways involving both tyrosine kinases and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases may be operative, the mechanisms of PMN priming are still not understood. We found that PMN priming was not achieved by treatment of cells with a very low concentration (5 ng/ml) of LPS unless additional "helper" factors were present in plasma (5%). Under these conditions, LPS induced tyrosine phosphorylation of a 38-kDa protein, which was coincident with the MAP kinase p38 action in this situation. LPS-mediated activation of p38 in human PMNs was dependent on the presence of LPS binding protein from plasma and CD14 on the surfaces of the cells. Phosphorylation of p38 was highly correlated with LPS priming of a formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP)-stimulated PMN respiratory burst. Treatment of PMN with the p38-specific inhibitor SB203580 significantly attenuated the respiratory burst in cells primed by LPS and stimulated by fMLP. These results suggest that the LPS signaling pathway leading to p38 activation may be an important mechanism in regulation of PMN priming. The mediator(s) linking CD14 to p38 involves proteins that are functionally sensitive to genistein but insensitive to tyrphostin AG126 and to Src- and Syk-family kinase, protein kinase C, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. Elucidating this pathway will provide insight into possible regulation of PMN priming by LPS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38) in beta 2-integrin-dependent neutrophil adhesion and the adhesion-dependent oxidative burst.J Immunol. 1998 Aug 15;161(4):1921-9. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9712062
-
Activation of extracellular signal-related protein kinases 1 and 2 of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family by lipopolysaccharide requires plasma in neutrophils from adults and newborns.Infect Immun. 2001 May;69(5):3143-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.3143-3149.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11292734 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades during priming of human neutrophils by TNF-alpha and GM-CSF.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Oct;64(4):537-45. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9766635
-
The Src family kinases Hck and Fgr regulate neutrophil responses to N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine.J Immunol. 2007 Mar 15;178(6):3874-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.6.3874. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17339487 Free PMC article.
-
Priming and de-priming of neutrophil responses in vitro and in vivo.Eur J Clin Invest. 2018 Nov;48 Suppl 2:e12967. doi: 10.1111/eci.12967. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29896919 Review.
Cited by
-
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli triggers oxygen-dependent apoptosis in human neutrophils through the cooperative effect of type 1 fimbriae and lipopolysaccharide.Infect Immun. 2004 Aug;72(8):4570-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4570-4578.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15271917 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Endotoxin Tolerance Induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide on Inflammatory Responses in Neutrophils.Inflammation. 2020 Oct;43(5):1692-1706. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01243-8. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 32440987
-
A Common Genetic Variant in TLR1 Enhances Human Neutrophil Priming and Impacts Length of Intensive Care Stay in Pediatric Sepsis.J Immunol. 2016 Feb 1;196(3):1376-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500856. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26729809 Free PMC article.
-
CD14 and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are required for fibrillar A{beta}-stimulated microglial activation.J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 23;29(38):11982-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3158-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19776284 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein tyrosine kinase p53/56lyn in diminished lipopolysaccharide priming of formylmethionylleucyl- phenylalanine-induced superoxide production in human newborn neutrophils.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6455-62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6455-6462.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannerman, D. D., and S. E. Goldblum. 1999. Direct effects of endotoxin on the endothelium: barrier function and injury. Lab. Investig. 79:1181-1199. - PubMed
-
- Berton, G., S. R. Yan, L. Fumagalli, and C. A. Lowell. 1996. Neutrophil activation by adhesion: mechanisms and pathophysiological implications. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 26:160-177. - PubMed
-
- Bortolussi, R., K. Rajaraman, G. Qing, and R. Rajaraman. 1997. Fibronectin enhances in vitro lipopolysaccharide priming of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood 89:4182-4189. - PubMed
-
- Coffer, P. J., and L. Koenderman. 1997. Granulocyte signal transduction and priming: cause without effect? Immunol. Lett. 57:27-31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

