Novel 33-kilodalton lipoprotein from Mycobacterium leprae
- PMID: 12117918
- PMCID: PMC128180
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4106-4111.2002
Novel 33-kilodalton lipoprotein from Mycobacterium leprae
Abstract
A novel Mycobacterium leprae lipoprotein LpK (accession no. ML0603) was identified from the genomic database. The 1,116-bp open reading frame encodes a 371-amino-acid precursor protein with an N-terminal signal sequence and a consensus motif for lipid conjugation. Expression of the protein, LpK, in Escherichia coli revealed a 33-kDa protein, and metabolic labeling experiments and globomycin treatment proved that the protein was lipidated. Fractionation of M. leprae demonstrated that this lipoprotein was a membrane protein of M. leprae. The purified lipoprotein was found to induce production of interleukin-12 in human peripheral blood monocytes. The studies imply that M. leprae LpK is involved in protective immunity against leprosy and may be a candidate for vaccine design.
Figures
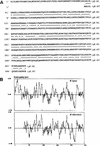



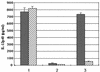
 ) polymyxin B, with LpK (columns 1), LpC (ML1699) (columns 2), and LPS (columns 3). lpc was identified from the database as a putative lipoprotein coding gene that was expressed and purified from inclusion bodies as a 39-kDa protein in E. coli. Values are expressed as the mean ± the standard deviation performed in triplicate.
) polymyxin B, with LpK (columns 1), LpC (ML1699) (columns 2), and LPS (columns 3). lpc was identified from the database as a putative lipoprotein coding gene that was expressed and purified from inclusion bodies as a 39-kDa protein in E. coli. Values are expressed as the mean ± the standard deviation performed in triplicate.Similar articles
-
Studies of lipoproteins of Mycobacterium leprae.Nihon Hansenbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Feb;73(1):15-21. doi: 10.5025/hansen.73.15. Nihon Hansenbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15035064 Review.
-
A 46 kDa integral membrane protein from Mycobacterium leprae resembles a number of bacterial and mammalian membrane transport proteins.Microbiology (Reading). 1995 Aug;141 ( Pt 8):1963-1968. doi: 10.1099/13500872-141-8-1963. Microbiology (Reading). 1995. PMID: 7551058
-
Antigenic proteins of Mycobacterium leprae. Complete sequence of the gene for the 18-kDa protein.J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):597-601. J Immunol. 1988. PMID: 2447183
-
A Mycobacterium leprae-specific gene encoding an immunologically recognized 45 kDa protein.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(4):829-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00953.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 7934845
-
Postgenomic Mycobacterium leprae antigens for cellular and serological diagnosis of M. leprae exposure, infection and leprosy disease.Lepr Rev. 2011 Dec;82(4):402-21. Lepr Rev. 2011. PMID: 22439280 Review.
Cited by
-
A lipopeptide facilitate induction of Mycobacterium leprae killing in host cells.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011 Nov;5(11):e1401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001401. Epub 2011 Nov 22. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011. PMID: 22132248 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and purification of an active form of the Mycobacterium leprae DNA gyrase and its inhibition by quinolones.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 May;51(5):1643-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01282-06. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17325221 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-Bound PenA β-Lactamase of Burkholderia pseudomallei.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Dec 28;60(3):1509-14. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02444-15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26711764 Free PMC article.
-
A database of bacterial lipoproteins (DOLOP) with functional assignments to predicted lipoproteins.J Bacteriol. 2006 Apr;188(8):2761-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.8.2761-2773.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16585737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cole, S. T., K. Eiglmeier, J. Parkhill, K. D. James, N. R. Thomson, P. R. Wheeler, N. Honore, T. Garnier, C. Churcher, D. Harris, K. Mungall, D. Basham, D. Brown, T. Chillingworth, R. Connor, R. M. Davies, K. Devlin, S. Duthoy, T. Feltwell, A. Fraser, N. Hamlin, S. Holroyd, T. Hornsby, K. Jagels, C. Lacroix, J. Maclean, S. Moule, L. Murphy, K. Oliver, M. A. Quail, M. A. Rajandream, K. M. Rutherford, S. Rutter, K. Seeger, S. Simon, M. Simmonds, J. Skelton, R. Squares, S. Squares, K. Stevens, K. Taylor, S. Whitehead, J. R. Woodward, and B. G. Barrell. 2001. Massive gene decay in the leprosy bacillus. Nature 409:1007-1010. - PubMed
-
- Dev, I. K., R. J. Harvey, and P. H. Ray. 1985. Inhibition of prolipoprotein signal peptidase by globomycin. J. Biol. Chem. 260:5891-5894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

