Roles of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, NF-kappaB, and protein kinase C in proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expression by human peripheral blood leukocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils in response to Anaplasma phagocytophila
- PMID: 12117921
- PMCID: PMC128199
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4132-4141.2002
Roles of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, NF-kappaB, and protein kinase C in proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expression by human peripheral blood leukocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils in response to Anaplasma phagocytophila
Abstract
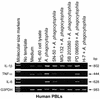
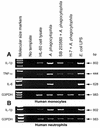
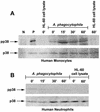
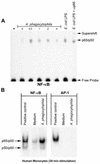
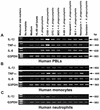
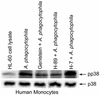
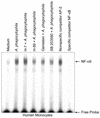
Anaplasma phagocytophila, an obligately intracellular bacterium of granulocytes, causes human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Within 2 h after addition of A. phagocytophila, interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and IL-6 mRNAs are induced in human peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs) or monocytes in vitro. However, neutrophils generate only IL-1beta mRNA. In the present study, signaling pathways for induction of these three cytokines were examined. TNF-alpha and IL-6 mRNA expression by PBLs was inhibited with SB 203580 (a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase [MAPK] inhibitor), MG-132 (a proteasome inhibitor), and SN-50 (an NF-kappaB inhibitor). Activation of p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB mRNAs in monocytes was detectable within 15 to 30 min after addition of A. phagocytophila. Expression of these two cytokine mRNAs in PBLs and monocytes was also dependent on protein kinase C (PKC), protein kinase A (PKA), and protein tyrosine kinase (PTK). IL-1beta mRNA expression by neutrophils was not dependent on p38 MAPK, and p38 MAPK was not activated in neutrophils incubated with A. phagocytophila. IL-1beta mRNA induction by PBLs, monocytes, and neutrophils was dependent on PKC and PKA. Neutrophil expression of IL-1beta mRNA was dependent on transglutaminase, phospholipase C, and PTK, all of which are also required for internalization of A. phagocytophila. However, monocyte expression of IL-1beta mRNA was less dependent on these enzymes. These results suggest that A. phagocytophila transduces different signals between its host neutrophils and monocytes for proinflammatory cytokine generation.
Figures
References
-
- Akiyama, T., and H. Ogawara. 1991. Use and specificity of genistein as inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 201:362-370. - PubMed
-
- Alessi, D. R., A. Cuenda, P. Cohen, D. T. Dudley, and A. R. Saltiel. 1995. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 270:27489-27494. - PubMed
-
- Bakken, J. S., J. Krueth, C. Wilson-Nordskog, R. L. Tilden, K. Asanovich, and J. S. Dumler. 1996. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. JAMA 275:199-205. - PubMed
-
- Bakken, J. S., J. Krueth, R. L. Tilden, J. S. Dumler, and R. E. Kristansen. 1996. Serologic evidence of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in Norway. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 15:829-832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

