Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice are more susceptible to staphylococcal enterotoxin B-mediated toxic shock than uninfected mice despite reduced in vitro splenocyte responses to superantigens
- PMID: 12117923
- PMCID: PMC128208
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4148-4157.2002
Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice are more susceptible to staphylococcal enterotoxin B-mediated toxic shock than uninfected mice despite reduced in vitro splenocyte responses to superantigens
Abstract
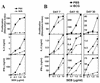
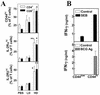
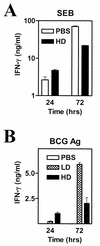
Type 1 T-cell responses against intracellular pathogens play a crucial role in mediating protection. We examined whether the induction of a strong type 1 T-cell response during a chronic bacterial infection influences responses to superantigens capable of inducing acute shock. Intravenous infection of mice with Mycobacterium bovis BCG appeared to induce a progressive anergy towards staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) and towards antigen preparation of BCG (BCG-Ag) itself, based on diminished gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production by SEB- and BCG-Ag-stimulated splenocytes from infected mice. In contrast to these in vitro results, injection of SEB into BCG-infected mice led to a dramatic increase in the serum IFN-gamma levels and the death of infected but not of control mice. In vitro hyporesponsiveness towards SEB and BCG-Ag occurred only with unfractionated splenocyte cultures, as purified T cells from infected mice produced higher levels of IFN-gamma. Hyporesponsiveness towards SEB and BCG-Ag in unfractionated splenocyte cultures was not due to suppressive antigen-presenting cells (APCs), as APCs from infected mice stimulated higher levels of IFN-gamma from purified T cells. The diminished IFN-gamma levels observed with bulk splenocytes appear to be due to changes in the T-cell-to-APC ratio that result in a decreased proportion of T cells, coupled to reduced proliferative responses and an increased susceptibility of effector T cells to activation-induced cell death in vitro. Our results indicate that the reported phenomena of T-cell anergy during mycobacterial infection may be an in vitro consequence of the development of a strong type 1 response in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of a novel in vitro co-culture system for studying host response to native bacterial antigens.J Immunol Methods. 1998 Feb 1;211(1-2):147-58. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)00200-7. J Immunol Methods. 1998. PMID: 9617839
-
Activation and re-activation potential of T cells responding to staphylococcal enterotoxin B.Int Immunol. 1995 Jul;7(7):1065-77. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.7.1065. Int Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8527404
-
Immune response to Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette Guérin infection in major histocompatibility complex class I- and II-deficient knock-out mice: contribution of CD4 and CD8 T cells to acquired resistance.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Feb;25(2):377-84. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250211. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7875199
-
Immunoregulatory mechanisms of T-cell-dependent shock induced by a bacterial superantigen in mice.Infect Immun. 1996 Sep;64(9):3443-5. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.9.3443-3445.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8751882 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Gram-positive bacterial superantigen outside-in signaling causes toxic shock syndrome.FEBS J. 2011 Dec;278(23):4649-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08151.x. Epub 2011 May 19. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21535475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IFN-gamma induces the erosion of preexisting CD8 T cell memory during infection with a heterologous intracellular bacterium.J Immunol. 2008 Aug 1;181(3):1700-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.3.1700. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18641306 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG)-Induced Protection in Brain Disorders.Inflammation. 2024 Dec;47(6):1902-1917. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02018-1. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38664351 Review.
References
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Baschieri, S., R. K. Lees, A. R. Lussow, and H. R. MacDonald. 1993. Clonal anergy to staphylococcal enterotoxin B in vivo: selective effects on T cell subsets and lymphokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 23:2661-2666. - PubMed
-
- Beno, D. W., M. R. Uhing, M. Goto, Y. Chen, V. A. Jiyamapa-Serna, and R. E. Kimura. 2001. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B potentiates LPS-induced hepatic dysfunction in chronically catheterized rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 280:G866-G872. - PubMed
-
- Blank, C., A. Luz, S. Bendigs, A. Erdmann, H. Wagner, and K. Heeg. 1997. Superantigen and endotoxin synergize in the induction of lethal shock. Eur. J. Immunol. 27:825-833. - PubMed
-
- Callard, R., A. J. George, and J. Stark. 1999. Cytokines, chaos, and complexity. Immunity 11:507-513. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

