Role of Yops and adhesins in resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica to phagocytosis
- PMID: 12117925
- PMCID: PMC128122
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4165-4176.2002
Role of Yops and adhesins in resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica to phagocytosis
Abstract
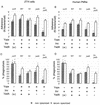
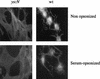
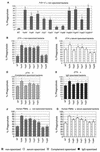
Yersinia enterocolitica is a pathogen endowed with two adhesins, Inv and YadA, and with the Ysc type III secretion system, which allows extracellular adherent bacteria to inject Yop effectors into the cytosol of animal target cells. We tested the influence of all of these virulence determinants on opsonic and nonopsonic phagocytosis by PU5-1.8 and J774 mouse macrophages, as well as by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). The adhesins contributed to phagocytosis in the absence of opsonins but not in the presence of opsonins. In agreement with previous results, YadA counteracted opsonization. In every instance, the Ysc-Yop system conferred a significant level of resistance to phagocytosis. Nonopsonized single-mutant bacteria lacking either YopE, -H, -T, or -O were phagocytosed significantly more by J774 cells and by PMNs. Opsonized bacteria were phagocytosed more than nonopsonized bacteria, and mutant bacteria lacking either YopH, -T, or -O were phagocytosed significantly more by J774 cells and by PMNs than were wild-type (WT) bacteria. Opsonized mutants lacking only YopE were phagocytosed significantly more than were WT bacteria by PMNs but not by J774 cells. Thus, YopH, -T, and -O were involved in all of the phagocytic processes studied here but YopE did not play a clear role in guarding against opsonic phagocytosis by J774. Mutants lacking YopP and YopM were, in every instance, as resistant as WT bacteria. Overexpression of YopE, -H, -T, or -O alone did not confer resistance to phagocytosis, although it affected the cytoskeleton. These results show that YopH, YopT, YopO, and, in some instances, YopE act synergistically to increase the resistance of Y. enterocolitica to phagocytosis by macrophages and PMNs.
Figures


References
-
- Aderem, A., and D. Underhill. 1999. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:593-623. - PubMed
-
- Andersson, K., N. Carballeira, K. Magnusson, C. Persson, O. Stendahl, H. Wolf-Watz, and M. Fallman. 1996. YopH of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis interrupts early phosphotyrosine signalling associated with phagocytosis. Mol. Microbiol. 20:1057-1069. - PubMed
-
- Andor, A., K. Trulzsch, M. Essler, A. Roggenkamp, A. Wiedemann, J. Heesemann, and M. Aepfelbacher. 2001. YopE of yersinia, a GAP for Rho GTPases, selectively modulates Rac-dependent actin structures in endothelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 3:301-310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

