Streptococcus suis interactions with the murine macrophage cell line J774: adhesion and cytotoxicity
- PMID: 12117940
- PMCID: PMC128179
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4312-4322.2002
Streptococcus suis interactions with the murine macrophage cell line J774: adhesion and cytotoxicity
Abstract
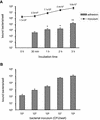
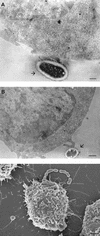
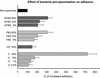
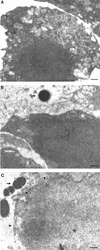
Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 is an important etiological agent of swine meningitis, and it is also a zoonotic agent. Since one hypothesis of the pathogenesis of S. suis infection is that bacteria enter the bloodstream and invade the meninges and other tissues in close association with mononuclear phagocytes, the objective of the present study was to evaluate the capacity of S. suis type 2 to adhere to macrophages. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique was standardized to simply and accurately measure the rate of bacterial attachment to phagocytic cells. Results were confirmed by plate counting. Adhesion was dependent on bacterial concentration and incubation time and was not affected by cytochalasin pretreatment of macrophages. Inhibition studies showed that the sialic acid moiety of the S. suis capsule would be, at least in part, responsible for bacterial recognition by macrophages. Serum preopsonization of bacteria increased adhesion levels. Complement would be partially implicated in the serum-enhanced binding of S. suis to cells. Adhesion varied among different S. suis type 2 isolates. However, high bacterial concentrations of several isolates were cytotoxic for cells, and these cytotoxic effects correlated with suilysin production. Indeed, hemolytic strain supernatants, as well as purified suilysin, reproduced cytotoxic effects observed with live bacteria, and these effects were inhibited by cholesterol pretreatment. Bacterial adhesion and cytotoxicity were confirmed by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. We hypothesize that attachment of bacteria to phagocytes could play an important role in the pathogenesis of S. suis infection by allowing bacterial dissemination and causing a bacteremia and/or septicemia. This interaction could also be related to the activation of the host inflammatory response observed during meningitis.
Figures
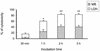
Similar articles
-
Polysaccharide capsule and suilysin contribute to extracellular survival of Streptococcus suis co-cultivated with primary porcine phagocytes.Vet Microbiol. 2008 Nov 25;132(1-2):211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 May 14. Vet Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18565698
-
Interactions between Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and different epithelial cell lines.Microbiology (Reading). 2000 Aug;146 ( Pt 8):1913-1921. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-8-1913. Microbiology (Reading). 2000. PMID: 10931895
-
Subcytolytic effects of suilysin on interaction of Streptococcus suis with epithelial cells.Vet Microbiol. 2013 Dec 27;167(3-4):584-91. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24095145
-
Biological activities of suilysin: role in Streptococcus suis pathogenesis.Future Microbiol. 2016 Jul;11:941-54. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0028. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Future Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27357518 Review.
-
Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis.Future Microbiol. 2012 Feb;7(2):259-79. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.149. Future Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22324994 Review.
Cited by
-
Streptococcus suis Induces Macrophage M1 Polarization and Pyroptosis.Microorganisms. 2024 Sep 12;12(9):1879. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12091879. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39338553 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulated Streptococcus suis inhibits activation of signaling pathways involved in phagocytosis.Infect Immun. 2004 Sep;72(9):5322-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5322-5330.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15322029 Free PMC article.
-
Heat incubation inactivates streptococcal exotoxins and recombinant cholesterol-dependent cytolysins: suilysin, pneumolysin and streptolysin O.Curr Microbiol. 2014 Nov;69(5):690-8. doi: 10.1007/s00284-014-0639-z. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Curr Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24974216
-
Novel variant serotype of streptococcus suis isolated from piglets with meningitis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Feb;81(3):976-85. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02962-14. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25416757 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of ICAM-1, CD11a/CD18 and CD11c/CD18 on human THP-1 monocytes stimulated by Streptococcus suis serotype 2.Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Jul;133(1):67-77. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02189.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12823280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaudoin, M., R. Higgins, J. Harel, and M. Gottschalk. 1992. Studies on a murine model for evaluation of virulence of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 isolates. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 78:111-116. - PubMed
-
- Brazeau, C., M. Gottschalk, S. Vincelette, and B. Martineau-Doize. 1996. In vitro phagocytosis and survival of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 inside murine macrophages. Microbiology 142:1231-1237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

