Inflammatory cytokines enhance the interaction of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin with bovine peripheral blood neutrophils in vitro
- PMID: 12117943
- PMCID: PMC128205
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4336-4343.2002
Inflammatory cytokines enhance the interaction of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin with bovine peripheral blood neutrophils in vitro
Abstract
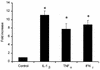
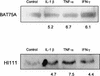
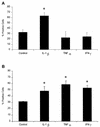
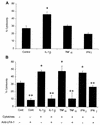
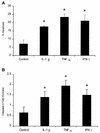
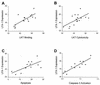
Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica A1 produces several virulence factors that play an important role in the pathogenesis of bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Foremost among these is a leukotoxin (LKT) that specifically kills ruminant leukocytes. Recent evidence suggests that M. haemolytica LKT binding to bovine leukocytes is mediated by the beta(2)-integrin CD11a/CD18 (lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 [LFA-1]), which subsequently induces activation and cytolysis of these cells. Inflammatory cytokines, which are released during viral and bacterial infection, are reported to increase LFA-1 expression and conformational activation. We investigated the effects of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) on the interaction of M. haemolytica LKT with bovine peripheral blood neutrophils (PMNs). In this study we demonstrated, by flow cytometry, that bovine PMNs increased their binding to an anti-bovine LFA-1 monoclonal antibody (BAT75A) following in vitro incubation with IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, or IFN-gamma. Incubation with cytokines also increased CD18 expression, as assessed by real-time PCR and by Western blotting. Increased LFA-1 expression by PMNs exposed to cytokines was associated with increased LKT binding and cytotoxicity. The latter represented, at least in part, enhanced PMN apoptosis, as assessed by propidium iodine staining and caspase-3 activation. The results of this study suggest that inflammatory cytokines may play an important role in enhancing the biological response of bovine PMNs to M. haemolytica LKT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prior exposure to Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin or LPS enhances beta(2)-integrin expression by bovine neutrophils and augments LKT cytotoxicity.Microb Pathog. 2003 Jun;34(6):267-75. doi: 10.1016/s0882-4010(03)00060-3. Microb Pathog. 2003. PMID: 12782479
-
BHV-1 infection and inflammatory cytokines amplify the interaction of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin with bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004 Jun;99(3-4):193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2004.02.004. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004. PMID: 15135985
-
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 is a receptor for Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin in bovine leukocytes.Infect Immun. 2000 Jan;68(1):72-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.72-79.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10603370 Free PMC article.
-
Complexities of the pathogenesis of Mannheimia haemolytica and Haemophilus somnus infections: challenges and potential opportunities for prevention?Anim Health Res Rev. 2004 Dec;5(2):277-82. doi: 10.1079/ahr200483. Anim Health Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 15984339 Review.
-
Mannheimia haemolytica: bacterial-host interactions in bovine pneumonia.Vet Pathol. 2011 Mar;48(2):338-48. doi: 10.1177/0300985810377182. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Vet Pathol. 2011. PMID: 20685916 Review.
Cited by
-
Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin induces apoptosis of bovine lymphoblastoid cells (BL-3) via a caspase-9-dependent mitochondrial pathway.Infect Immun. 2005 Sep;73(9):5504-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5504-5513.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16113266 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of impaired protein kinase C signaling by chemokines in murine macrophages during visceral leishmaniasis.Infect Immun. 2005 Dec;73(12):8334-44. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8334-8344.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16299331 Free PMC article.
-
14-Deoxyandrographolide desensitizes hepatocytes to tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis through calcium-dependent tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A release via the NO/cGMP pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;160(7):1823-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00836.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20649583 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-2 and caspase-7 are involved in cytolethal distending toxin-induced apoptosis in Jurkat and MOLT-4 T-cell lines.Infect Immun. 2004 Feb;72(2):871-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.871-879.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14742531 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-gamma activation of polymorphonuclear neutrophil function.Immunology. 2004 May;112(1):2-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01849.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15096178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambagala, T. C., A. P. N. Ambagala, and S. Srikumaran. 1999. The leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica binds to β2 integrin on bovine leukocytes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 179:161-167. - PubMed
-
- Baluyut, C. S., R. R. Simonson, W. J. Bemrick, and S. K. Maheswaran. 1981. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am. J. Vet. Res. 42:1920-1926. - PubMed
-
- Billiau, A., and F. Vandekerckhove. 1991. Cytokines and their interaction with other inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of sepsis and septic shock. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 21:559-573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

