Mobilization of protein kinase C in macrophages induced by Listeria monocytogenes affects its internalization and escape from the phagosome
- PMID: 12117979
- PMCID: PMC128209
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4650-4660.2002
Mobilization of protein kinase C in macrophages induced by Listeria monocytogenes affects its internalization and escape from the phagosome
Abstract
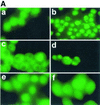
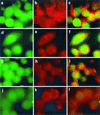
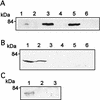
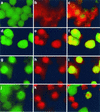
Listeriolysin O (LLO) and a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) are known virulence factors of Listeria monocytogenes in both tissue cultures and the murine model of infection. LLO is a member of a family of pore-forming cholesterol-dependent cytotoxins and is known to play an essential role in escape from the primary phagocytic vacuole of macrophages. PI-PLC plays an accessory role, in that PI-PLC mutants are partially defective in escape. We have shown that both of these molecules are essential for initiating rapid increases in the calcium level in the J774 murine macrophage cell line (S. J. Wadsworth and H. Goldfine, Infect. Immun. 67:1770-1778, 1999). Here we show that both LLO and PI-PLC are required for translocation of protein kinase C delta (PKC delta) to the periphery of J774 cells and for translocation of PKC beta II to early endosomes beginning within the first minute after addition of bacteria to the culture medium. Treatment with the calcium channel blocker SK&F 96365 inhibited translocation of PKC beta II but not PKC delta. Our findings lead us to propose a host signaling pathway requiring LLO and the formation of diacylglycerol by PI-PLC in which calcium-independent PKC delta is responsible for the initial calcium signal and the subsequent PKC beta II translocation. LLO-dependent translocation of PKC beta I to early endosomes also occurs between 1 and 4 min after infection, but this occurs in the absence of PI-PLC. All of these signals were observed in cells that had not internalized bacteria. Blocking PKC beta translocation with hispidin resulted in more rapid uptake of wild-type bacteria and greatly reduced escape from the primary phagocytic vacuoles of J774 cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Activation of host phospholipases C and D in macrophages after infection with Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2000 Oct;68(10):5735-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.10.5735-5741.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10992479 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes phospholipase C-dependent calcium signaling modulates bacterial entry into J774 macrophage-like cells.Infect Immun. 1999 Apr;67(4):1770-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.4.1770-1778.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10085017 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of Listeria monocytogenes PI-PLC to facilitate escape from the macrophage phagosome is dependent on host PKCbeta.Microb Pathog. 2009 Jan;46(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2008.09.008. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Microb Pathog. 2009. PMID: 18996181 Free PMC article.
-
Listeriolysin O: A phagosome-specific cytolysin revisited.Cell Microbiol. 2019 Mar;21(3):e12988. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12988. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Cell Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30511471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Listeria species escape from the phagosomes of interleukin-4-deactivated human macrophages independent of listeriolysin.Immunol Cell Biol. 2003 Dec;81(6):431-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2003.01196.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14636240 Review.
Cited by
-
The Application of Cinnamon Twig Extract as an Inhibitor of Listeriolysin O against Listeria monocytogenes Infection.Molecules. 2023 Feb 8;28(4):1625. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041625. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838612 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of the Listeria monocytogenes broad-range phospholipase PC-PLC during infection of human epithelial cells.J Bacteriol. 2003 Nov;185(21):6295-307. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.21.6295-6307.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 14563864 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted activity of listeriolysin O, the cholesterol-dependent cytolysin of Listeria monocytogenes.Subcell Biochem. 2014;80:161-95. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8881-6_9. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24798012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell sequencing of the substantia nigra reveals microglial activation in a model of MPTP.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jun 17;16:1390310. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1390310. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38952478 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells form suppurative granulomas following Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Clin Invest. 2006 Dec;116(12):3160-70. doi: 10.1172/JCI28996. Epub 2006 Nov 16. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17111046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Dominguez, C., A. M. Barbieri, W. Berón, A. Wandinger-Ness, and P. D. Stahl. 1996. Phagocytosed live Listeria monocytogenes influences rab5-regulated in vitro phagosome-endosome fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 271:13834-13843. - PubMed
-
- Bubert, A., Z. Sokolovic, S. K. Chun, L. Papatheodorou, A. Simm, and W. Goebel. 1999. Differential expression of Listeria monocytogenes virulence genes in mammalian host cells. Mol. Gen. Genet. 261:323-336. - PubMed
-
- Bucci, C., R. G. Parton, I. H. Mather, H. Stunnenberg, K. Simons, B. Hoflack, and M. Zerial. 1992. The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell 70:715-728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

