Escherichia coli shiga-like toxins induce apoptosis and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase via in vitro activation of caspases
- PMID: 12117981
- PMCID: PMC128130
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4669-4677.2002
Escherichia coli shiga-like toxins induce apoptosis and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase via in vitro activation of caspases
Abstract
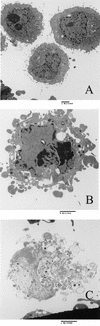
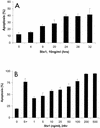
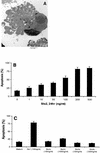
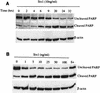
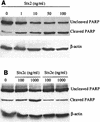
Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli causes hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic-uremic syndrome in association with the production of Shiga-like toxins, which induce cell death via either necrosis or apoptosis. However, the abilities of different Shiga-like toxins to trigger apoptosis and the sequence of intracellular signaling events mediating the death of epithelial cells have not been completely defined. Fluorescent dye staining with acridine orange and ethidium bromide showed that Shiga-like toxin 1 (Stx1) induced apoptosis of HEp-2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Stx2 also induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Apoptosis induced by Stx1 (200 ng/ml) and apoptosis induced by Stx2 (200 ng/ml) were maximal following incubation with cells for 24 h (94.3% +/- 1.8% and 81.7% +/- 5.2% of the cells, respectively). Toxin-treated cells showed characteristic features of apoptosis, including membrane blebbing, DNA fragmentation, chromatin condensation, cell shrinkage, and the formation of apoptotic bodies, as assessed by transmission electron microscopy. Stx2c induced apoptosis weakly even at a high dose (1,000 ng/ml for 24 h; 26.7% +/- 1.3% of the cells), whereas Stx2e did not induce apoptosis of HEp-2 cells. Thin-layer chromatography confirmed that HEp-2 cells express the Stx1-Stx2-Stx2c receptor, globotriaosylceramide (Gb3), but not the Stx2e receptor, globotetraosylceramide (Gb4). Western blot analysis of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), a DNA repair enzyme, demonstrated that incubation with Stx1 and Stx2 induced cleavage, whereas incubation with Stx2e did not result in cleavage of PARP. A pan-caspase inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK) and a caspase-8-specific inhibitor (Z-IETD-FMK) eliminated, in a dose-dependent fashion, the cleavage of PARP induced by Shiga-like toxins. Caspase-8 activation was confirmed by detection of cleavage of this enzyme by immunoblotting. Cleavage of caspase-9 and the proapoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family BID was also induced by Stx1, as determined by immunoblot analyses. We conclude that different Shiga-like toxins induce different degrees of apoptosis that correlates with toxin binding to the glycolipid receptor Gb3 and that caspases play an integral role in the signal transduction cascade leading to toxin-mediated programmed cell death.
Figures

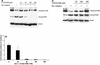


References
-
- Abreu, M. T., A. A. Palladino, E. T. Arnold, R. S. Kwon, and J. A. McRoberts. 2000. Modulation of barrier function during Fas-mediated apoptosis in human intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 119:1524-1536. - PubMed
-
- Agbodaze, D. 1999. Verocytotoxins (Shiga-like toxins) produced by Escherichia coli: a minireview of their classification, clinical presentations and management of a heterogeneous family of cytotoxins. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22:221-230. - PubMed
-
- Arab, S., M. Murakami, P. Dirks, B. Boyd, S. L. Hubbard, C. A. Lingwood, and J. T. Rutka. 1998. Verotoxins inhibit the growth of and induce apoptosis in human astrocytoma cells. J. Neurooncol. 40:137-150. - PubMed
-
- Belmokhtar, C. A., J. Hillion, and E. Segal-Bendirdjian. 2001. Staurosporine induces apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms. Oncogene 20:3354-3362. - PubMed
-
- Braun, J. S., R. Novak, K. H. Herzog, S. M. Bodner, J. L. Cleveland, and E. I. Tuomanen. 1999. Neuroprotection by a caspase inhibitor in acute bacterial meningitis. Nat. Med. 5:298-302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

