Orientia tsutsugamushi inhibits apoptosis of macrophages by retarding intracellular calcium release
- PMID: 12117985
- PMCID: PMC128204
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4692-4696.2002
Orientia tsutsugamushi inhibits apoptosis of macrophages by retarding intracellular calcium release
Abstract
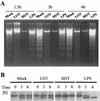
Orientia tsutsugamushi shows both pro- and antiapoptotic activities in infected vertebrate cells. Apoptosis of THP-1 cells induced by beauvericin was inhibited by O. tsutsugamushi infection. Beauvericin-induced calcium redistribution was significantly reduced and retarded in cells infected with O. tsutsugamushi. Antiapoptotic activities of O. tsutsugamushi in infected cells are most probably due to inhibition of the increase in the cytosolic calcium concentration.
Figures

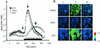
References
-
- Balcewicz-Sablinska, M. K., J. Keane, H. Kornfeld, and H. G. Remold. 1998. Pathogenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis evades apoptosis of host macrophages by release of TNF-R2, resulting in inactivation of TNF-α. J. Immunol. 161:2636-2641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

