Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by human corneal epithelial cells: role of bacterial fibronectin-binding protein and host cell factors
- PMID: 12117986
- PMCID: PMC128182
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4697-4700.2002
Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by human corneal epithelial cells: role of bacterial fibronectin-binding protein and host cell factors
Abstract
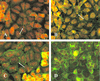
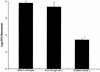
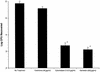
Wild-type Staphylococcus aureus was observed to be capable of invading human corneal epithelial cells (HCEC) in vitro. Internalization of S. aureus required expression of fibronectin-binding proteins (FnBPs); the capacity of an FnBP-deficient isogenic strain to invade HCEC was reduced by more than 99%. The binding of S. aureus to HCEC did not require viable bacteria, since UV-killed cells were observed to adhere efficiently. Invasion of HCEC by S. aureus involved active host cell mechanisms; uptake was nearly completely eliminated by cytochalasin D and genistein. These data suggest that FnBPs play a key role in host-parasite interactions and may serve as an important adhesin or invasin in ulcerative keratitis caused by S. aureus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host-parasite interactions in Staphylococcus aureus keratitis.DNA Cell Biol. 2002 May-Jun;21(5-6):397-404. doi: 10.1089/10445490260099683. DNA Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12167242
-
Fibronectin binding protein and host cell tyrosine kinase are required for internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 1999 Sep;67(9):4673-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4673-4678.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10456915 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin-binding protein acts as Staphylococcus aureus invasin via fibronectin bridging to integrin alpha5beta1.Cell Microbiol. 1999 Sep;1(2):101-17. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.1999.00011.x. Cell Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 11207545
-
The role of fibronectin binding proteins in the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus infections.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003 Jun;16(3):225-9. doi: 10.1097/00001432-200306000-00007. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12821812 Review.
-
Sticky connections: extracellular matrix protein recognition and integrin-mediated cellular invasion by Staphylococcus aureus.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006 Feb;9(1):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.12.002. Epub 2006 Jan 6. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16406780 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infectious keratitis: key bacterial mechanisms that mediate pathogenesis and emerging therapeutics.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 21;13:1250257. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1250257. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37671149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the transmembrane mucins MUC1 and MUC16 in epithelial barrier function.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 26;9(6):e100393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100393. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24968021 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Warfare on Three Fronts: Mixed Biofilm of Aspergillus fumigatus and Staphylococcus aureus on Primary Cultures of Human Limbo-Corneal Fibroblasts.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Aug 16;11:646054. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.646054. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34485167 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune response of corneal epithelial cells to Staphylococcus aureus infection: role of peptidoglycan in stimulating proinflammatory cytokine secretion.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Oct;45(10):3513-22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0467. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. PMID: 15452057 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effect of URP20 on ocular Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli infection in rats.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec 30;22(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02752-w. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36585631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed, S., S. Meghji, R. J. Williams, B. Henderson, J. H. Brock, and S. P. Nair. 2001. Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin binding proteins are essential for internalization by osteoblasts but do not account for differences in intracellular levels of bacteria. Infect. Immun. 69:2872-2877. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araki-Sasaki, K., Y. Ohashi, T. Sasabe, K. Hayashi, H. Watanabe, Y. Tano, and H. Handa. 1995. An SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line and its characterization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 36:614-621. - PubMed
-
- Foster, T. J., and M. Höök. 1998. Surface protein adhesins of Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 6:484-488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

